FIG 2.
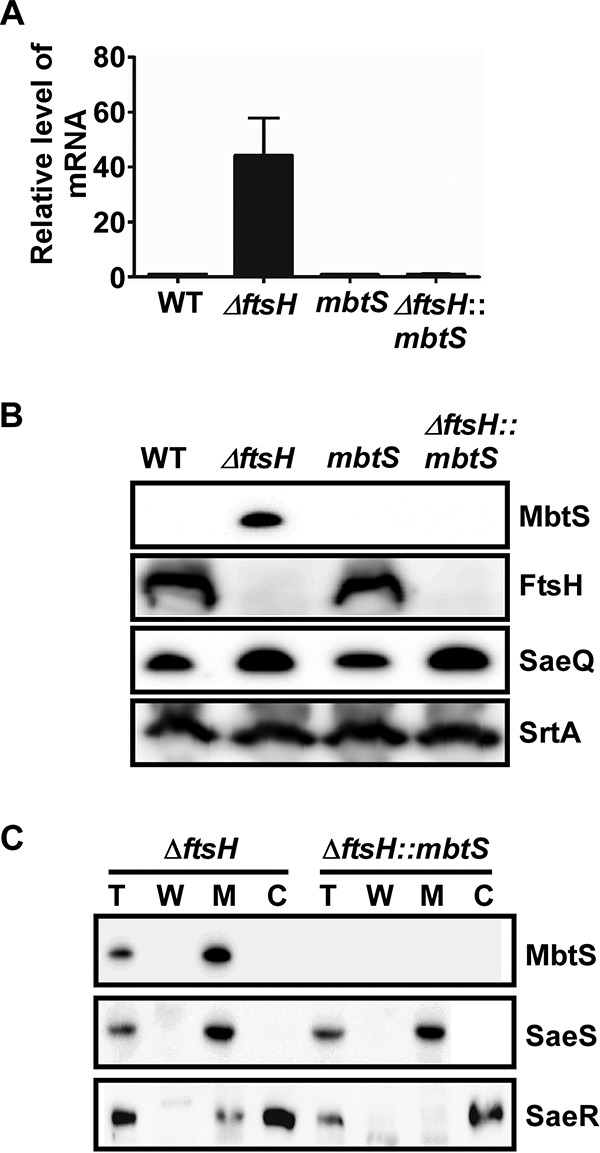
MbtS is a membrane-bound transcription factor regulated by FtsH. (A and B) Effect of the ftsH deletion on the expression of mbtS at the levels of the transcript (A) and the protein (B). The test strains were grown in TSB until the exponential growth phase, and then total RNA and proteins were prepared from whole-cell lysates as detailed in Materials and Methods. The transcript levels were determined by qRT-PCR, whereas the protein levels were determined by Western blotting. In the Western blot analysis, the membrane protein SaeQ, an FtsH substrate, was used to monitor the FtsH activity, whereas the membrane protein SrtA (sortase A), a non-FtsH substrate, was used as a negative control. WT, wild-type USA300; ΔftsH, ftsH deletion mutant; mbtS, USA300 with a transposon insertion at mbtS; ΔftsH::mbtS, ftsH deletion mutant with a transposon insertion at mbtS. The original Western blots are provided in Fig. S1 in the supplemental material. (C) Membrane localization of MbtS. Cells were grown until exponential growth phase, collected by centrifugation, and converted into protoplasts by lysostaphin treatment in the presence of 0.5 M sucrose. The supernatant was designated the cell wall fraction (W). The protoplasts were further lysed and subjected to ultracentrifugation, and the supernatant was designated the cytoplasm (C), whereas the pellet was washed and designated the membrane (M). The proteins were detected by Western blotting with cognate antibodies. The detected proteins are indicated on the right side of the blot. The sensor histidine kinase SaeS, a membrane protein, and the response regulator SaeR, a cytoplasmic protein, were used as fractionation controls. Sometimes a low level of SaeR is detected in the membrane fraction, possibly due to its interaction with SaeS. T, total protein.
