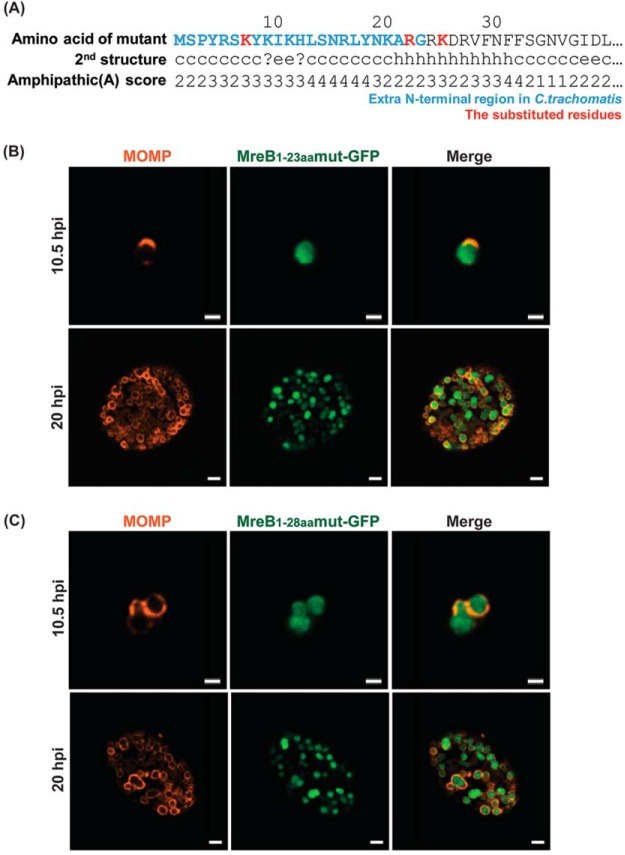
FIG 6.
Localization in C. trachomatis of various mutated N-terminal regions of chlamydial MreB fused to GFP. (A) Mutations were introduced into the N-terminal region of chlamydial MreB and modeled for their effect on amphipathicity. L7K, L22R, and F25K (red residues) mutations disrupted the predicted amphipathicity (see Fig. 2 for comparison). (B) C. trachomatis serovar L2 without plasmid (−pL2) was transformed with anhydrotetracycline (aTc)-inducible vectors encoding the mutated chlamydial MreB1-23aa-GFP or MreB1-28aa-GFP fusion peptide. HeLa cells were infected with the indicated strains, and expression of the GFP fusions was induced at 6 hpi or 16 hpi with 10 nM aTc. At 10.5 hpi or 20 hpi, the samples were fixed (3.2% formaldehyde, 0.022% glutaraldehyde in 1× PBS) for 2 min and permeabilized with 90% methanol (MeOH) for 1 min. These samples were stained for major outer membrane protein (MOMP; red) with GFP imaged in green. Images were acquired on a Zeiss Imager.Z2 equipped with an Apotome2 using a 100× lens objective. Bars, 1 μm (10.5 hpi) or 2 μm (20 hpi).