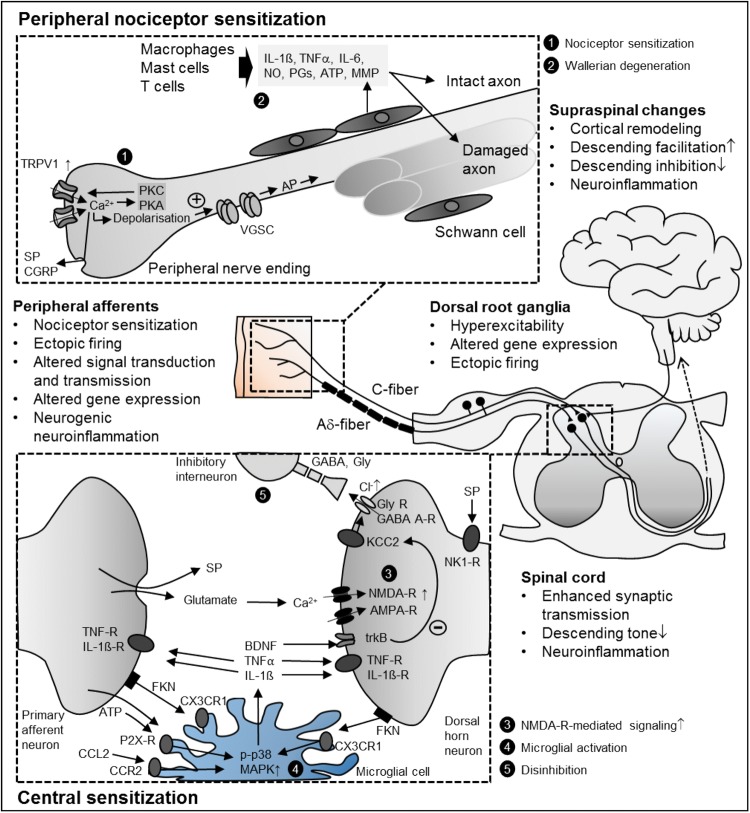
Fig. 1.
Selection of peripheral and central mechanisms contributing to neuropathic pain. AMPA-R/NMDA-R ionotropic glutamate receptors, AP action potential, ATP adenosine triphosphate, BDNF brain-derived neurotrophic factor, CCL2/FKN chemokines, CCR2/CX3CR1 chemokine receptors, CGRP calcitonin gene-related peptide, GABA gamma-aminobutyric acid, Gly Glycin, FKN fractalkine (CX3CL1), IL-1β interleukin 1β, IL-6 interleukin 6, KCC2 chloride potassium symporter, MMP matrix metalloproteinase, NK1-R neurokinin 1 receptor, NO nitric oxide, p-p38 MAPK phosphorylated p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, PG prostaglandins, SP substance P, TNFα tumor necrosis factor-alpha, TNF-R tumor necrosis factor receptor, trkB tyrosine kinase B, TRPV1 transient receptor potential vanilloid 1, VGSC voltage-gated sodium channel