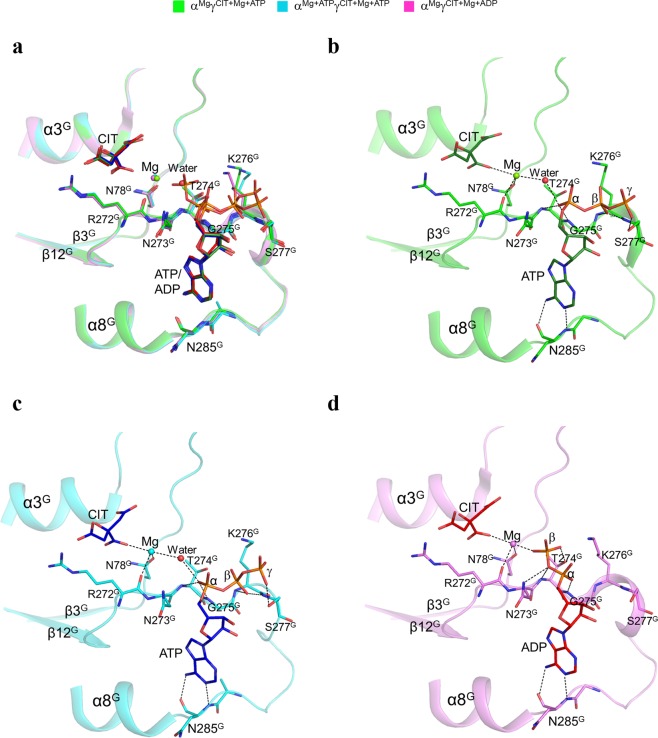
Figure 2.
Structures of the allosteric sites in the αMgγMg+CIT+ATP and αMg+ATPγMg+CIT+ATP structures. (a) Comparison of the allosteric site in the αMgγMg+CIT+ATP, αMg+ATPγMg+CIT+ATP, and αMgγMg+CIT+ADP structures. The key residues at the allosteric site in the αMgγMg+CIT+ATP and αMg+ATPγMg+CIT+ATP structures assume very similar conformations as those in the active αMgγMg+CIT+ADP structure. The color scheme of the structures is shown above. (b) Structure of the allosteric site in the αMgγMg+CIT+ATP structure. (c) Structure of the allosteric site in the αMg+ATPγMg+CIT+ATP structure. (d) Structure of the allosteric site in the αMgγMg+CIT+ADP structure. The key residues and the CIT and ATP (or ADP) are shown with ball-and-stick models, and the Mg2+ and water molecules are shown with green and red spheres, respectively. Hydrogen-bonding interactions of ATP (or ADP) and Mg2+ with CIT and the surrounding residues are indicated with dotted lines.