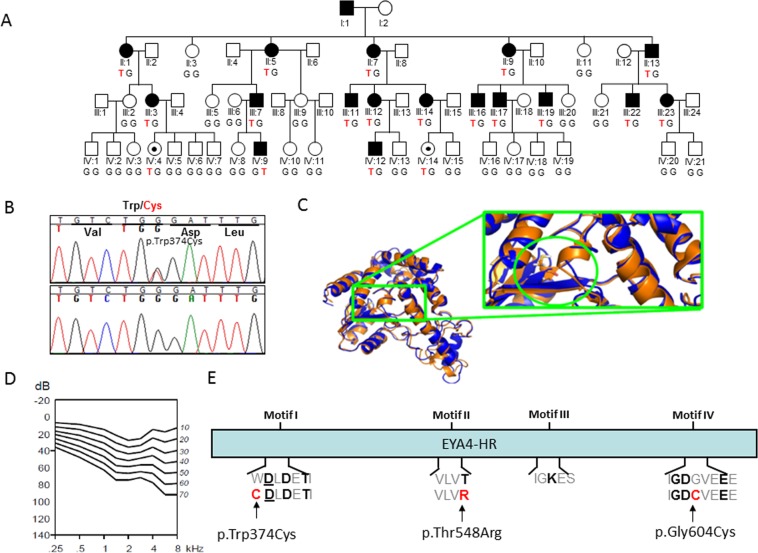
Figure 3.
(A) Pedigree of the family 10880 showing the novel EYA4 (c.1122G > T) variant segregating with the hearing loss phenotype. The genotype of all the subjects analysed is indicated in capital letters (Wt = GG, Hz = GT). Black dots represent normal hearing individuals carrying the mutation but under the age of onset in this family. (B) Representative chromatograms from wild-type and mutant sequences. (C) Molecular modelling of the p.Trp374Cys in EYA4. Mutated site is highlighted by a green circle and locally zoomed. Mutant (orange) is superimposed on wild-type (blue) for comparison. The p.Trp374Cys alters local conformation and disrupts beta sheet backbone folding resulting in decrease structural stability. (D) Age Related Typical Audiogram (ARTA) analysis. The hearing loss progresses at a rate that ranges between 0.5 dB/year at 0.25Khz and 1.3 dB/year at 8 kHz. E) EYA4-HR domain showing the four Tyr-phosphatase motifs that mediate the protein enzymatic activity. The p.Trp374Cys mutation identified in this work, and two previously identified missense mutations (p.Thr548Arg and p.Gly604Cys) are all affecting conserved residues at motif I, II and IV, respectively.