Figure 7.
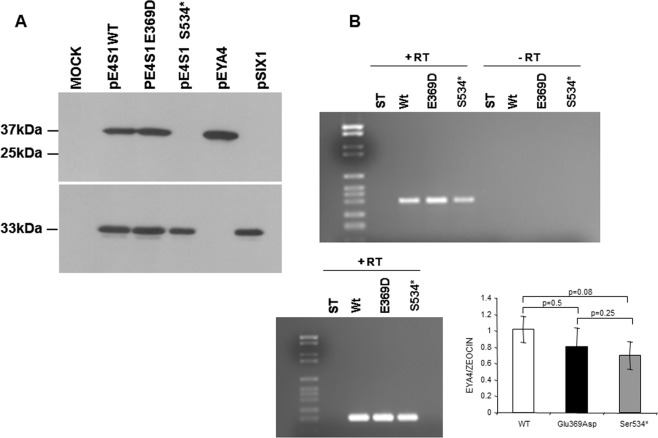
(A) Western blot analysis of EYA4 Wt and mutants’ production. A clear band of 37 kDa corresponding to the EYA4-HR domain detected by the anti-myc antibodies directed against the c-myc tag cloned in frame in the Nt portion of the EYA4-HR domain (Suppl Fig. 1) is observed in extracts from COS7 cells transfected with pE4S1 Wt and Glu369Asp bicistronic plasmid and in the control pEYA4. No signal was detected in the mutant Ser534* when we use the same anti-Myc antibodies (at the top), whereas a robust band of 33kDA corresponding to SIX1 was seen when we use anti-HA antibodies (at the bottom) to detect the HA-tagged SIX1 protein (Suppl Fig. 1). The full-length blots revealed at different time exposures with anti-Myc and anti-HA antibodies are displayed in Suppl Fig. 5. (B) (top) RT-PCR assay performed on total RNA extracted from COS7 cells transfected with Eya constructs (wild-type and mutants) showed a band corresponding to the amplification of the tagged EYA4-HR mRNA. This band was not detected in the control lanes (-RT) in which the mRNA was nod added; (B) (bottom) cDNA amplification of Zeocin (the plasmid antibiotic resistant cassette) using specific primer was used for normalization purposes. Quantification of the relative amounts of EYA4 cDNA amplifications once they were normalized with Zeocin levels did not show any statistically significant differences after Wt and mutants comparisons. t Student p values are shown.