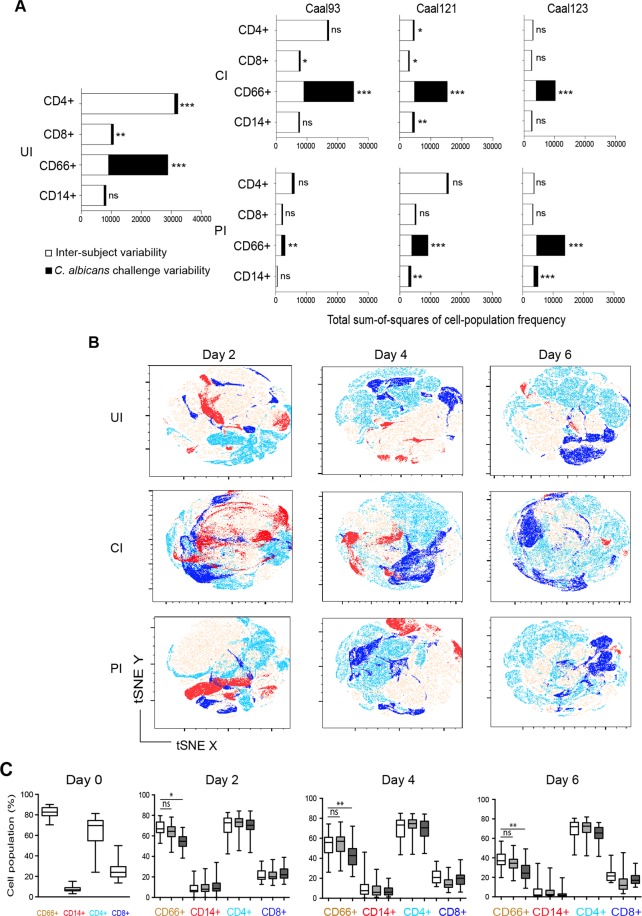
Figure 4.
C. albicans post-challenge changes in the immune cell composition. (A) Variation in CD4+, CD8+, CD3+, CD66+ and CD14+ cell subpopulation frequencies after C. albicans challenge. An ANOVA model was fitted to assess what fraction of the observed variance of immune cell frequency is due to differences among subjects (inter-subject variability, white boxes) or to C. albicans challenge variability (black boxes) in comparison to unstimulated cells on day 0. The inter-subject variability was quantified within the columns as the sum of squares of differences between each subject and the sixteen subjects mean. The post-challenge variability was quantified as the sum of squares of the differences between the column means and the grand mean. The F ratio was the ratio of two sum of square values. Large F ratio signified higher post-challenge variability than inter-subject variability. The P value was determined from the F ratio and the two values of degrees of freedom. The relative contributions of inter-subject variability and C. albicans challenge to the total observed variation in the immune parameters was measured on Prism 6.0a by calculating the range of subject-to-subject differences (total sum-of-squares), n = 16, p ≤ 0.05. Immune cells frequencies data were analyzed according to UI controls, CI and PI outcomes for Caal93, Caal121 and Caal123 clinical isolates. (B) Global phenotypic modifications of immune cells induced by C. albicans over the post-challenge time. Data from all of subjects and clinical isolates were concatenated and analyzed on tSNE FlowJo module according to PI and CI outcomes and UI controls. Phenotype clustering shows CD66+ (beige), CD14+ (red), CD4+ (light blue), CD8+ (dark blue) immune cells expression. (C) Composition of C. albicans – leucocyte cocultures. The proportions of CD66+, CD14+, CD4+ and CD8+ cells were expressed as a percentage of the total living cell compartment. Box plots depict median, minimum, and maximum percentages of immune cells according to UI (white boxes) uninfected control, CI (light gray) and PI (dark gray) outcomes and on days 0, 2, 4 and 6 after challenge with C. albicans. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.001; ***P < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test (n = 16). ns, not significant.