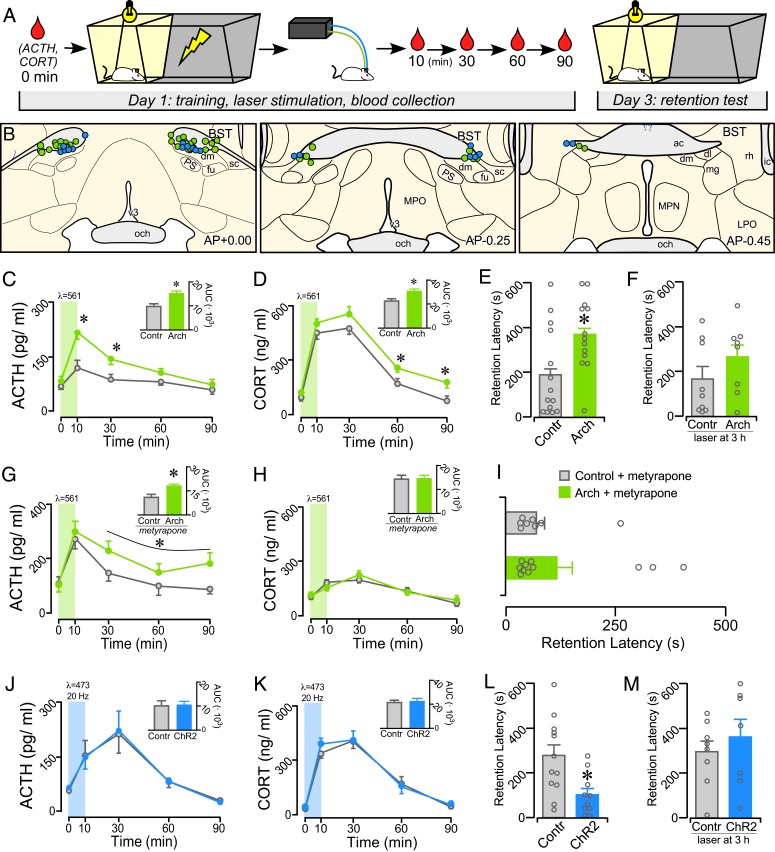
Fig. 1.
Posttraining manipulation of avBST activity bidirectionally modulates IA memory consolidation. (A) Diagram illustrating the experimental time line. Posttraining inhibition and stimulation of the avBST were conducted in serial experiments and were compared with AAV5-YFP control rats receiving identical illumination, respectively. (B) Examples of fiber optic implants targeted toward the region immediately dorsal to the avBST for illumination. Circles represent rats from separate experiments, first for Arch inhibition (green, n = 13; n = 11 for metyrapone + Arch group in G–I), and next for ChR2 activation (blue, n = 10) of avBST neurons. Coronal atlas images adapted from Swanson (93). (C and D) Shown are mean ± SEM of plasma ACTH (C) and CORT (D) in control and Arch groups before (0 min) and at various intervals following IA training. Both hormones are significantly increased in the Arch group at various intervals following illumination. (C and D, Inset) Integrated ACTH and CORT responses (AUC) were also significantly increased in the Arch versus YFP groups. (E and F) Inhibition of avBST neurons in the Arch group immediately posttraining increased retention latencies when measured 48 h later (E), but not when inhibition was administered 3-h posttraining (F). (G and H) Mean ± SEM of plasma ACTH and CORT in control and Arch groups before (0 min) and at various intervals following IA training following pretreatment with a glucocorticoid synthesis blocker (metyrapone). Inhibition of avBST with Arch potentiated the increase in plasma ACTH levels, whereas CORT levels were not distinguishable between Arch and control groups due to pretreatment with metyrapone. (G and H, Inset) Integrated ACTH and CORT responses (AUC) in Arch and YFP groups. (I) Posttraining inhibition of avBST neurons failed to enhance retention latencies when assessed 48 h later. (J and K) Plasma levels of ACTH (J) and CORT (K) were not significantly altered by posttraining activation of avBST neurons with ChR2. (L and M) ChR2 rats displayed significantly decreased retention latencies relative to YFP controls (L) when assessed 48 h later, whereas stimulation with ChR2 at 3-h posttraining had no effect (M). *P < 0.05. ac, anterior commissure; dl, BST dorsolateral subdivion; dm, avBST dorsomedial subdivision; fu, avBST fusiform subdivision; LPO, lateral preoptic area; mg, BST magnocellular subdivision; MPN, median preoptic nucleus; MPO, medial preoptic area; och, optic chiasm; PS, parastrial nucleus; rh, BST rhomboid subdivision; sc, avBST subcommissural subdivision.