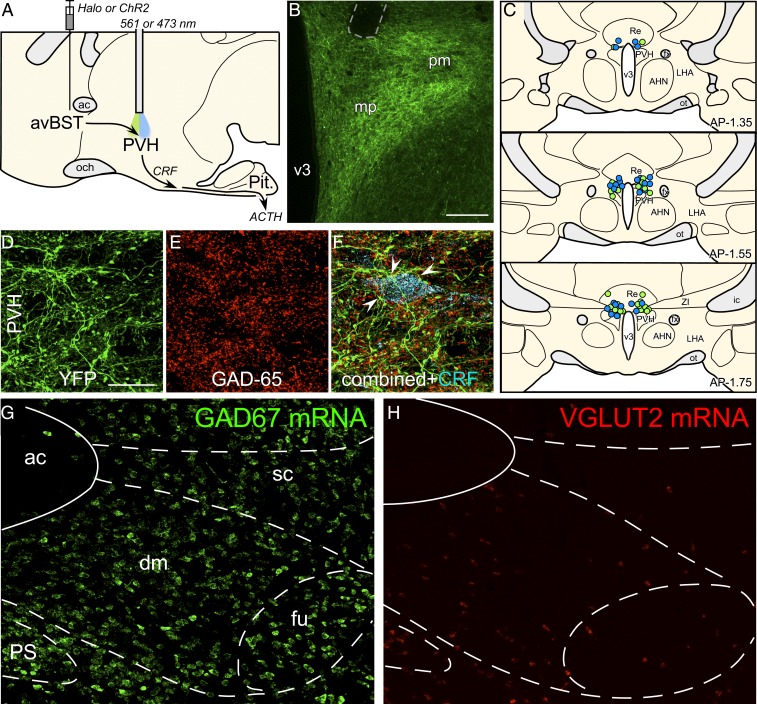
Fig. 3.
Role of avBST–GABAergic input to PVH in the enhancement of memory consolidation. (A) Midsagittal diagram depicting AAV5 microinjection into avBST and fiber optic placement above the PVH to assess avBST→PVH pathway involvement in the posttraining modulation of HPA activity and consolidation of IA learning. (B) Fluorescent image illustrating the distribution of YFP-labeled terminal fields in PVH following injection in the avBST. Fiber optic implant is shown by dashed gray outline in the upper left. (Scale bar, 200 µm.) (C) Examples of fiber optic implants targeted toward the region immediately dorsal to the PVH for illumination. Different colored circles represent rats from separate experiments, first for Halo inhibition (green, n = 15), and next for ChR2 activation (blue, n = 15) of the avBST→PVH axonal pathway. (D) Confocal fluorescent images depict YFP immunoreactivity in the medial parvicellular subdivision of the PVH following AAV injection in avBST, and GAD-65, the 65-kDa form of GAD, a synthetic enzyme for GABA (E). (F) Composite of images in D and F, with the addition of immunolocalization of CRF (cyan). Numerous instances of YFP+/GAD+ puncta were noted to make appositions with CRF-labeled neurons (arrowheads). (G and H) Fluorescent images showing in situ hybridization of GAD67 (G) and VGLUT2 (H) mRNA in avBST and its vicinity. ac, anterior commissure; AHA, anterior hypothalamic area; dm, avBST dorsomedial subdivision; fu, avBST fusiform subdivision; LHA, lateral hypothalamic area; mp, PVH medial parvicellular subdivision; och, optic chiasm; ot, optic tract; Pit., pituitary gland; pm, PVH posterior magnocellular subdivision; PS, parastrial nucleus; Re, nucleus reunions; sc, avBST subcommissural subdivision; v3, third ventricle. (Scale bar in D: 20 µm when applied to D–F; 100 µm when applied to G and H.)