Fig. 3.
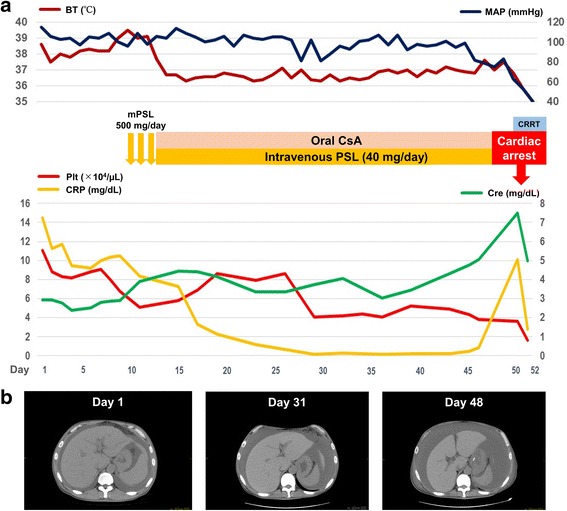
Clinical course of the present case. a, b The patient became afebrile after pulse methylprednisolone therapy. The C-reactive protein (CRP) level decreased to within the normal range with combination therapy involving intravenous glucocorticoid and oral cyclosporine A. However, despite the treatment, the amount of ascites increased gradually and renal impairment did not improve. The CRP and serum creatinine levels were elevated on day 50, and complicated infection was suspected. After the initiation of continuous renal replacement therapy, the patient experienced cardiac arrest on the same day because of myocardial infarction. Despite intensive care, including antibiotics therapy and continuous hemodiafiltration, the patient died on day 52. BT body temperature, Cre creatinine, CRP C-reactive protein, CRRT continuous renal replacement therapy, CsA cyclosporine A, MAP mean arterial pressure, mPSL methylprednisolone, Plt platelet
