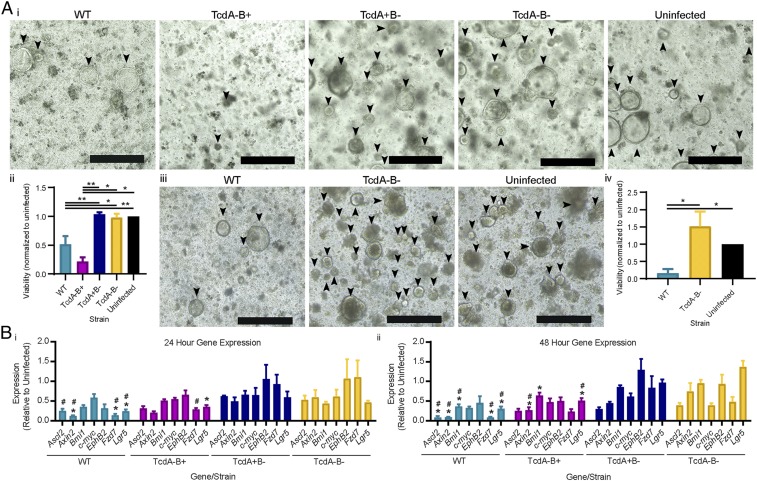
Fig. 2.
C. difficile TcdB alters murine colonic stem cell function and gene expression. Equal numbers of colonic crypts isolated from tissues collected postinfection with WT, TcdA−B+, TcdA+B−, and TcdA−B− C. difficile, or uninfected mice were used to derive murine colonic organoids, at 24 or 48 h postinfection. (A, i) Representative images of organoids 24 h postinfection are shown, (ii) with cell viability assessed via a PrestoBlue assay. (iii) Representative images of mature organoids after 48 h of infection are shown, (iv) with cell viability assessed via a PrestoBlue assay. (B) Quantitative ddPCR analysis of colonic tissue (i) 24 h and (ii) 48 h postinfection. Gene expression, as fold change relative to uninfected mice, was plotted (*, significant difference compared to TcdA−B−; #, significant difference compared to TcdA+B−). Data are represented as mean + SEM, n > 4. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01. (Scale bars: 400 µm.) See also SI Appendix, Fig. S2.