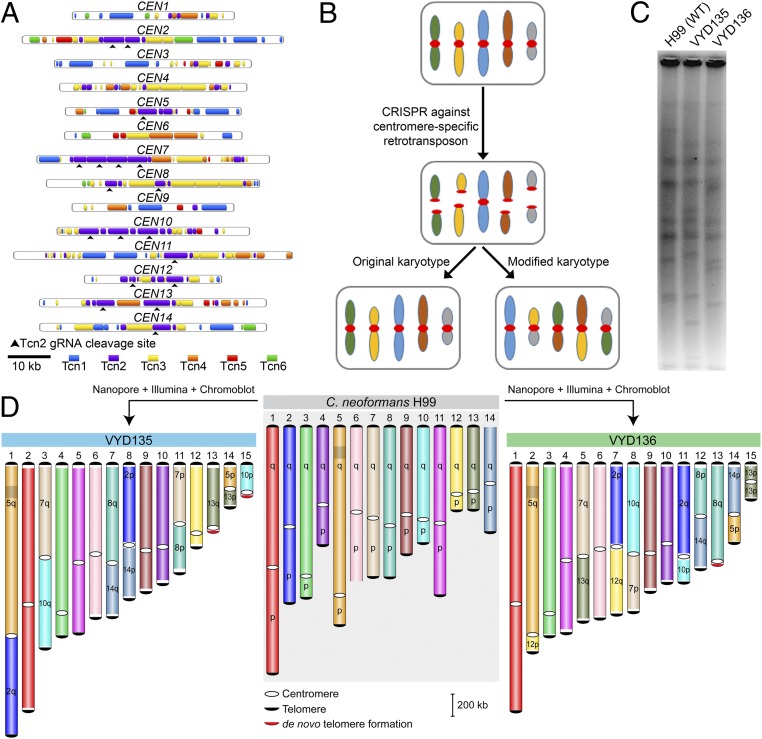
Fig. 1.
Centromere-specific DSBs mediated by CRISPR led to chromosome rearrangements. (A) Centromere maps showing the distribution of retrotransposons (Tcn1–Tcn6) in the centromeres of wild-type strain H99 of C. neoformans. (B) An outline depicting the model for achieving multiple chromosome translocations in C. neoformans. (C) PFGE revealed many differences in the karyotype of VYD135 and VYD136 compared with wild type, H99. (D) Chromosome maps for VYD135 and VYD136 compared to the H99 genome revealed multiple chromosome translocations in these strains. Chromosomes are colored with H99 chromosomes as reference. “q” represents the longer arm, while “p” represents the shorter arm according to the wild-type chromosome configuration.