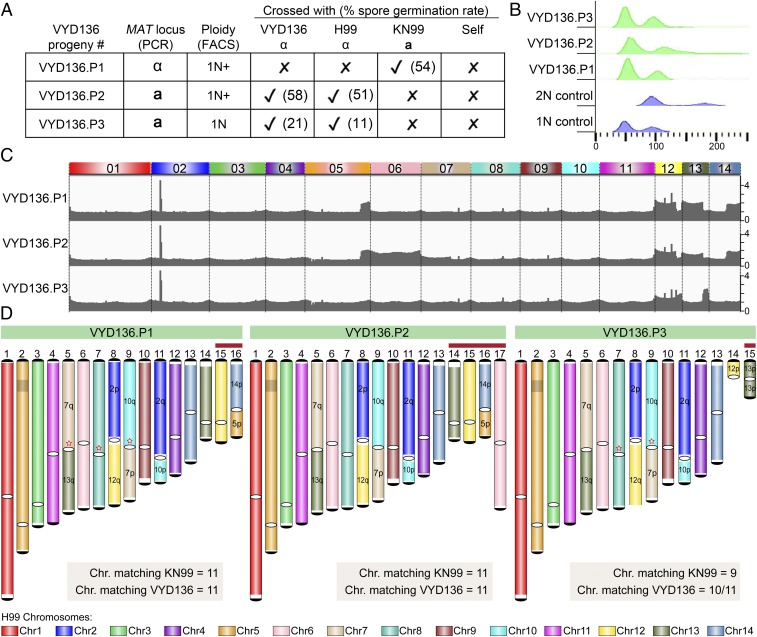
Fig. 6.
VYD136 progeny are aneuploid and exhibit mixed karyotypes. (A) Analysis of the mating-type locus and the mating efficiency of three progeny of VYD136 with either parent. The numbers in brackets represent spore germination rates of respective crosses. (B) Flow cytometry profiles of wild-type haploid, diploid, and three progeny of VYD136. (C) Illumina sequencing data mapped to the wild-type H99 genome revealed aneuploidy for multiple chromosomes in the three VYD136 progeny. (D) Karyotypes for three progeny showing synteny compared to the wild-type H99 genome. The red stars represent breaks that were fused later based on synteny and ploidy. The chromosomes shown with red bar on top were not assembled de novo but represent possible chromosomes configuration based on Illumina and nanopore sequencing analysis. Contigs 14 in VYD136.P3 could not be resolved into their chromosome configuration. “q” represents longer arm, while “p” represents shorter arm according to the wild-type chromosome configuration.