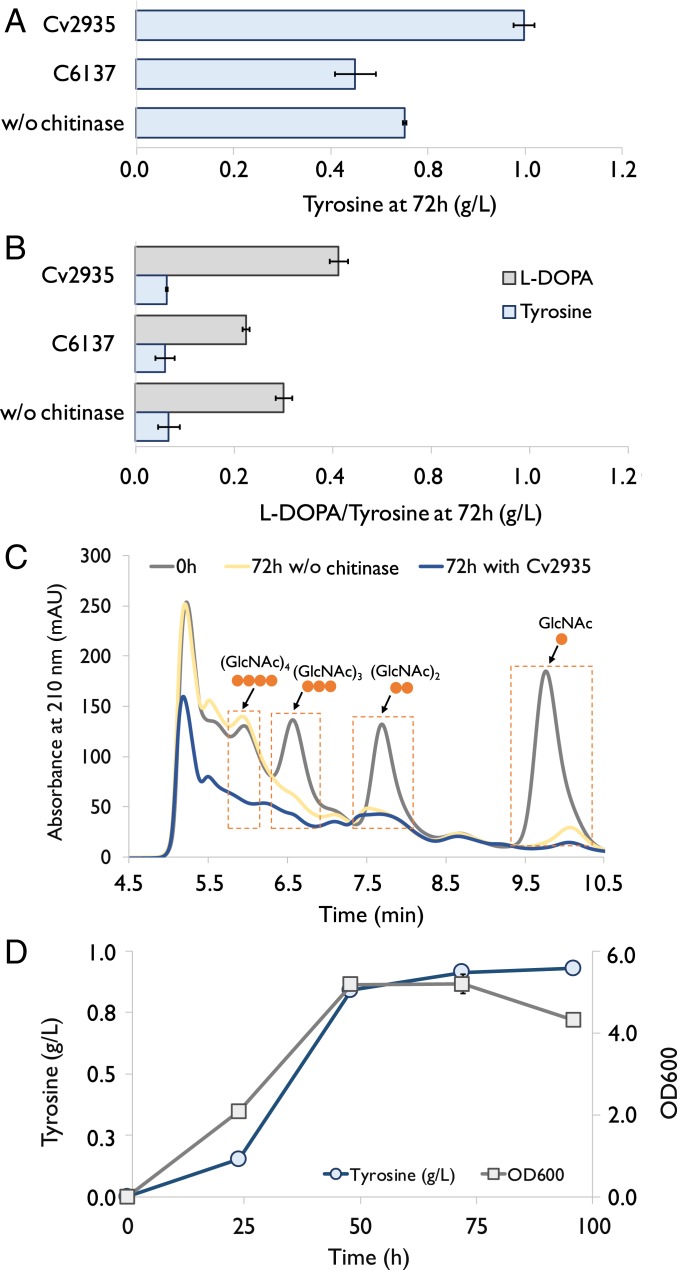
Fig. 6.
Production of tyrosine and l-DOPA using SSW-derived chitin hydrolysates as the sole carbon and nitrogen sources. (A) Tyrosine production by using the engineered E. coli strain carrying plasmid NP19 with or without adding chitinases. (B) l-DOPA production by using the engineered E. coli carrying plasmid LDOPA5 with or without adding chitinases. Cv2935 (4 μg/mL): chitinase from C. violaceum. C6137 (8.4 μg/mL): a commercialized chitinase from Streptomyces griseus (Sigma, C6137). (C) HPLC analysis of the consumption of GlcNAc and its oligomers by the engineered E. coli strain carrying plasmid NP19. 0h: at the beginning of the fermentation. “72 h w/o enzyme”: after 72 h since the beginning of the fermentation without adding any chitinase. “72 h with Cv2935”: after 72 h since the beginning of the fermentation with adding Cv2935 (10 μg/mL). (D) Time profile of tyrosine concentration and cell density (OD600) in the one-pot enzymatic/fermentative process. The engineered E. coli strain carrying plasmid NP19 was cultured by using 22.5 g/L SSW-derived chitin hydrolysates. Cv2935 (10 μg/mL) was added into the medium upon inoculation. Error bars indicate SE (n = 3).