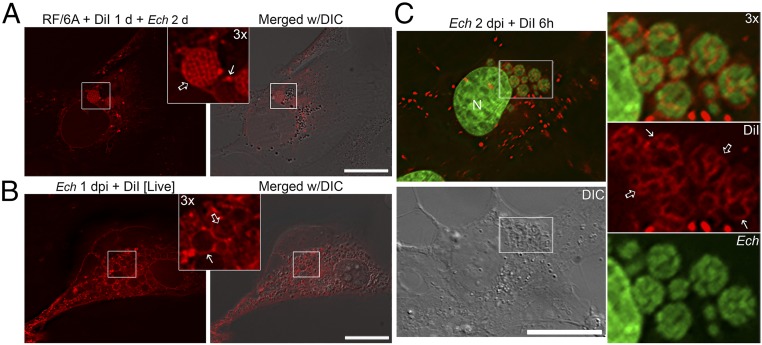
Fig. 2.
DiI-labeled host membranes are trafficked to membranes of E. chaffeensis inclusions, ILVs, and individual bacteria. (A) RF/6A cells were seeded on coverglasses in a six-well plate and incubated with 5 μM DiI for 1 d and washed three times with AMEM to remove excess dye. Cells were then infected with E. chaffeensis for 2 d. After washing, cells were fixed and observed under a DeltaVision microscope. Inlet shows 3× enlargement of the boxed area. Solid arrow, DiI-labeled inclusion membrane; open arrow, individual bacterial membranes. E. chaffeensis inclusions are visible under the DIC image. (B) RF/6A cells seeded on a 35-mm glass-bottom culture dish were infected with E. chaffeensis for 2 d. Cells were incubated with 5 μM DiI in serum-free, phenol red-free AMEM for 15 min and washed three times with AMEM to remove excess dye. Live cells were observed under a DeltaVision microscope in a heated environment. Inlet shows 3× enlargement of the boxed area. Solid arrow, inclusion membrane; open arrow, intrainclusional membranes. E. chaffeensis inclusions are visible under the DIC image. (C) RF/6A cells were seeded onto coverglasses in a 12-well plate for 1 d and then infected with E. chaffeensis for 2 d. Cells were labeled with 5 μM DiI for 6 h, fixed and stained with Hoechst 33342 (pseudocolored green), then observed under a DeltaVision microscope. The boxed area in the merged image is enlarged 3× on the right. Solid arrows, inclusion membrane; open arrows, individual bacterial membranes. Images from above panels are the representative of at least three independent experiments. (Scale bars, 10 μm.)