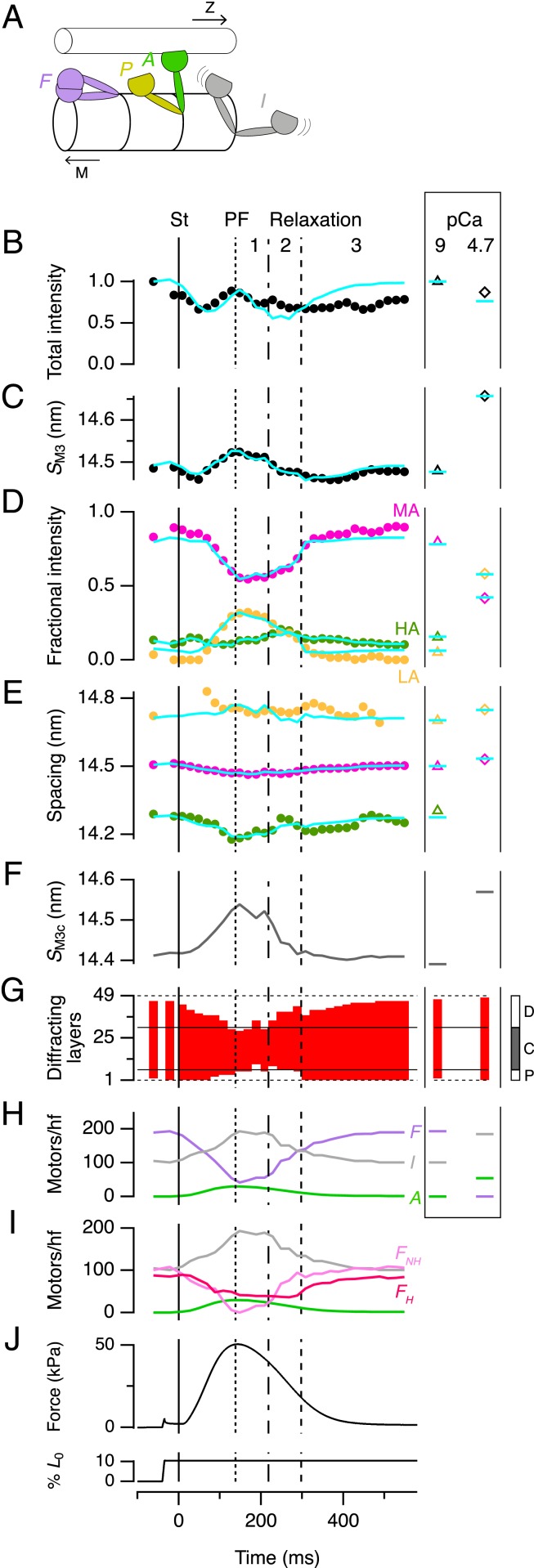
Fig. 6.
Determining the number of motors in standard conformations by X-ray interference. (A) Standard motor conformations: folded (F, purple), actin-attached (A, green), partner of an attached motor (P, yellow), and isotropic (I, gray). Toward filament midpoint, M; Z-band, Z. (B–E) Time courses of M3 intensity (IM3, B) and spacing (SM3, C), and the fractional intensity (D) and spacing (E) of its three component peaks with color code as in Fig. 5C. Data added from six trabeculae. St, stimulus. Vertical lines as in Fig. 2. (Right Inset) Values from demembranated trabeculae in relaxation (triangles) and full activation (diamonds); note that the HA peak cannot be measured at pCa 4.7. Cyan lines denote results from the calculations described in the text for the following parameters: (F) Spacing of the myosin motors in the C-zone (SM3c). (G) Diffracting layers of myosin motors (red vertical bars) and their position in the myosin half-filament as shown in the Inset at Right. (H) Number of motors folded, actin-attached and isotropic per half-filament; color code as in A. (I) The folded motors in H resolved into the maximum number in the helical array (FH, dark pink) and the remainder nonhelical motors (FNH, light pink). (J) Force and trabecular length change reproduced from Fig. 2A for reference.