Figure 9.
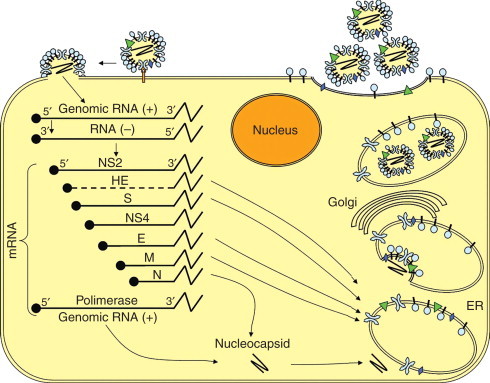
Schematic representation of the life cycle of a coronavirus. Virion binds receptors on the plasma membrane by the S glycoproteins resulting in fusion of viral envelope and plasma or endosomal membrane. ORF 1 of the genomic RNA is translated generating the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase that synthesizes negative-sense RNAs, which serve as templates to generate full-length genomic RNA and subgenomic (NS2, HE, S, NS4, E, M, and N). mRNAs are translated in structural and nonstructural proteins. The N protein and newly synthesized genomic RNA form the nucleocapsid. Other structural proteins are inserted in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) where they are cotranslationally glycosylated and trimerized. The nucleocapsids are then enclosed by these proteins in the ER and transported to the Golgi apparatus. Mature virions are apparently released by exocytosis-like fusion of smooth-walled vesicles with the plasma membrane.
