FIG 25.2.
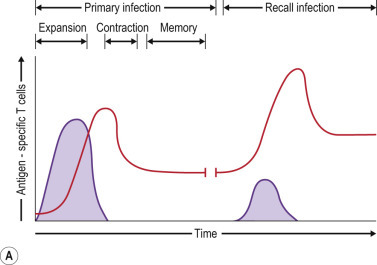
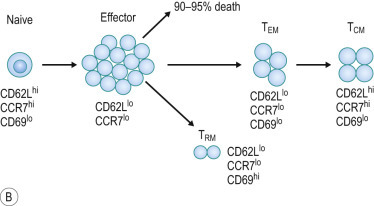
Expansion/Contraction/Memory Phases of Adaptive Immunity and Memory Cell Subsets.
(A) Dynamics of primary and secondary (recall) T-cell responses to viral infection. Both primary and recall T-cell responses undergo expansion and contraction phases, followed by stable immune memory. Recall responses induce a larger effector pool and reduced contraction further boosting the memory pool. (B) Effector and memory T-cell differentiation. Antigen stimulation expands effector cells, most of which die during the contraction phase. Effector memory T (TEM) cells that are formed gradually convert to central memory T (TCM) cells over time, with corresponding changes in surface marker expression. Some effector T cells develop into resident memory T (TRM) cells that persist in the tissues and do not reenter the circulation.
