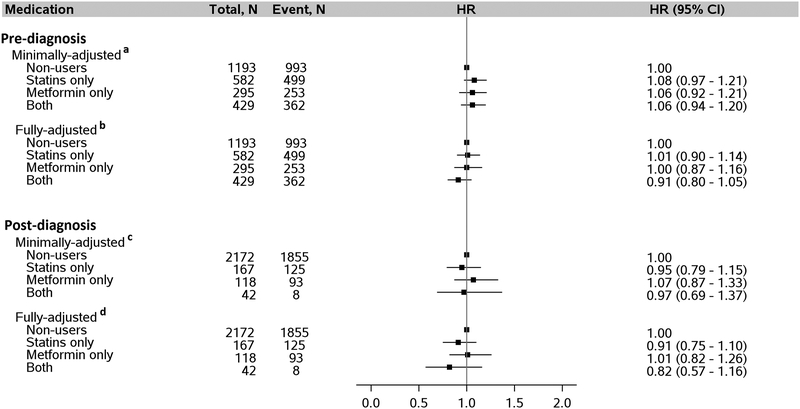
Figure 2:
Association between use of statins and/or metformin by patients with diabetes pre- and post-diagnosis of HCC and risk of death after HCC diagnosis. a Adjusted for age (continuous), sex, and post-diagnosis medication use (statins only, metformin only, both, neither). b Adjusted for everything in “a” plus year of diagnosis, race, marital status, neighborhood income level, percent with 4-year college in neighborhood, tumor grade, tumor stage, chemotherapy, radiation, Charlson comorbidity index, diabetes severity index, obesity, presence of COPD, dyslipidemia, and hepatitis as categorized in Table 1. c Adjusted for age, sex, and pre-diagnosis medication use (statins only, metformin only, both, neither). d Adjusted for everything in “c” with additional adjustment for year of diagnosis, race, marital status, neighborhood income level, percent with 4-year college in neighborhood, tumor grade, tumor stage, chemotherapy, radiation, Charlson comorbidity index, diabetes severity index, obesity, COPD, dyslipidemia, and hepatitis as categorized in Table 1. Abbreviation: HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma.