Table 3.
The therapy targeting NLRP3 inflammasome for AS.
| Therapy type | Medicine | Chemical structure | Effects and mechanisms | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural medicine | Artemisinin (50, 100 mg/kg) |
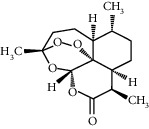
|
Vascular protection: the formation and proliferation of foam cells improved; the fibrosis in the intima of aorta promoted Inflammation inhibition: targeting the AMPK/NF-κB-NLRP3 pathway |
[99] |
| Rosmarinic acid (100 μM) |
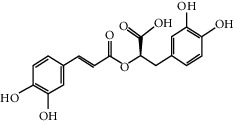
|
Playing a protective role in nicotine-induced AS via inhibiting the axis of ROS-NLRP3-CRP | [100] | |
| Curcumin (0–100 μM) |
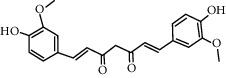
|
Inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome in PMA-induced macrophage by inhibiting TLR4/MyD88, NF-κB, and P2X2R | [101] | |
| UDCA (20 μg/ml) | — | Attenuating NLRP3-dependent inflammation: reducing CCs; increasing cholesterol solubility | [102] | |
| Berberine (75 μM) |
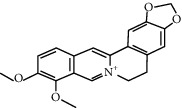
|
Alleviating NLRP3 inflammasome activation and reducing IL-1β secretion | [103] | |
| DHM (0.1, 0.5, and 1 μM) |
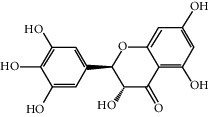
|
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities: ROS reduced; the release of caspase-1 and IL-1β reduced | [104] | |
| Apigenin (50 μM) |
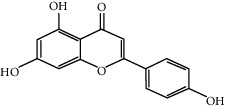
|
Endothelium protection: reversing the expression of adhesion molecule ICAM-1 and NLRP3 inflammasome | [105] | |
| Clinical medicine | Colchicine (1 mg followed by 0.5 mg 1 hour later) |
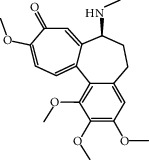
|
The levels of caspase-1 and IL-1β reduced | [106, 107] |
| Statins (atovastatin 0–40 μM) |
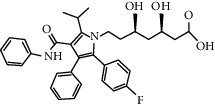
|
Inhibiting cholesterol synthesis; anti-inflammatory function | [108, 109] | |
| Dapagliflozin (1.0 mg/kg/d) |
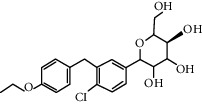
|
Inhibiting IL-1β secretion through the ROS-NLRP3-caspase-1 pathway | [110] | |
| Metformin (300 mg/kg/d, drinking water) |
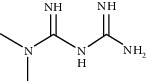
|
Anti-inflammatory function: reducing NLRP3 expression; inhibiting NLRP3 activation | [111] | |
|
| ||||
| Others | Dietary fiber | — | Antiatherogenic effects; anti-inflammatory effects | [112] |
| Dietary PUFAs | — | Activating macrophage autophagy; inhibiting the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome | [112] | |
| Melatonin (20–2000 μM) | — | Anti-inflammatory effects; preventing apoptosis of endothelial cells; attenuating NLRP3 inflammasome activation | [74] | |
AMPK: adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; CRP: C-reactive protein; PMA: phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate; UDCA: ursodeoxycholic acid; CCs: cholesterol crystals; DHM: dihydromyricetin; TMAO: trimethylamine N-oxide; PUFAs: dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids.
