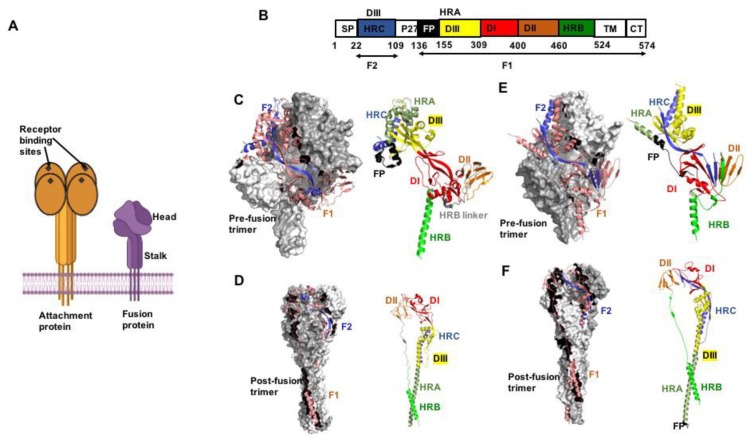
Figure 1.
The pneumo- and paramyxovirus entry machinery. (A) Schematic of paramyxovirus attachment and F proteins showing the overall head and stalk organization of the attachment protein tetramer and F protein trimer, respectively. (B) Color-coded schematic representation of the F protein domain organization (shown by example of RSV F). Heptad repeat (HR) domains A (HRA) and B (HRB) form the post- and prefusion F helical stalks, respectively. HR domain C (HRC) is located in the membrane-distal section of the prefusion F head. SP, signal peptide; FP, fusion peptide; TM, transmembrane domain; CT, cytoplasmic tail. The precursor F0 precursor protein is cleaved into F1 and F2 subunits. (C) Crystal structure of the prefusion PIV5 F trimer (PDB 4GIP). Surface view with one monomer shown as cartoon (left panel). F2 in blue and F1 in salmon. Domain view of a single monomer (right panel), colored as in (B). (D) Postfusion hPIV3 F trimer (PDB 1ZTM), the 6HB is oriented towards the base of the structure. (E,F) Pre- and postfusion forms of RSV F (PDB 4MMQ and 3RRR, respectively). Subtle differences in overall geometry to paramyxovirus F are present in the prefusion head specifically. All figures were prepared with PyMol (DeLano Scientific; http://pymol.sourceforge.net/).