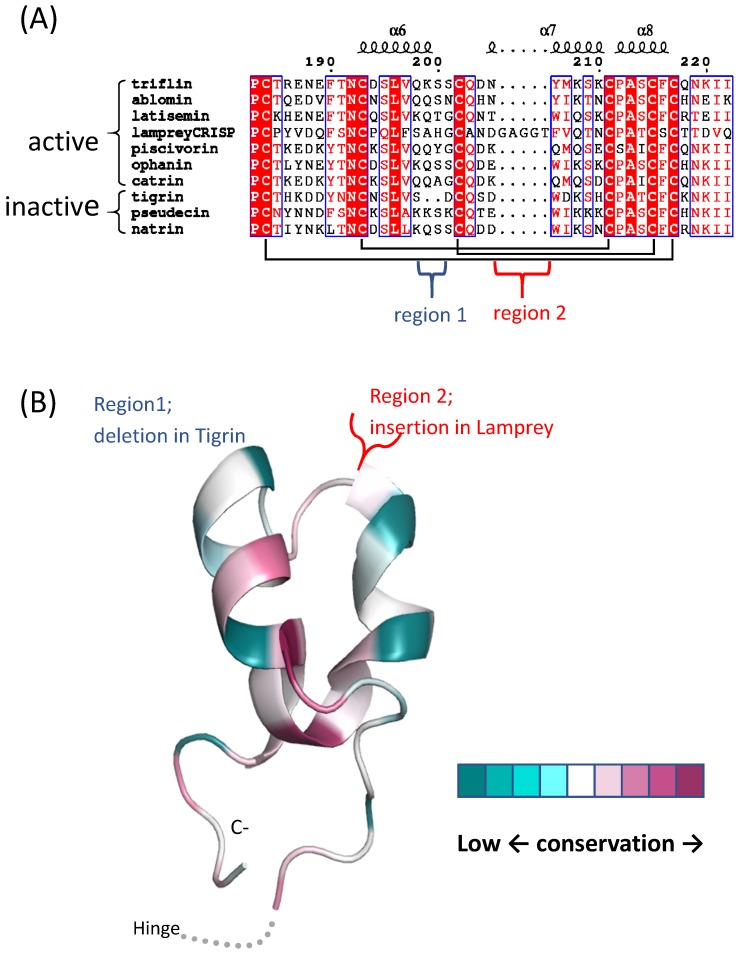
Figure 3.
Comparisons between CRD/ICR domain regions of CRISPs that inhibit ion channels and those that do not. (A) Amino-acid sequence alignment of CRD/ICR regions of CRISP family proteins, showing highly conserved residues highlighted in red, and other conserved residues in a red font. Cysteine residues forming disulfide bridges are indicated by black brackets. The secondary structure of triflin (PDB ID: 1WVR) is shown above the alignment. (B) Structural conservation in the CRD/ICR region of snake venom CRISPS (svCRISPs0 that inhibit high-potassium-induced contraction of smooth muscle is shown on a triflin scaffold (PDB ID: 1WVR). Conservation scores were calculated with the Consurf server using default settings. Conservation scores are graded on a nine-point scale, from the most variable positions (turquoise) to the most conserved positions (maroon). The structure was prepared using PyMOL (https://pymol.org/).