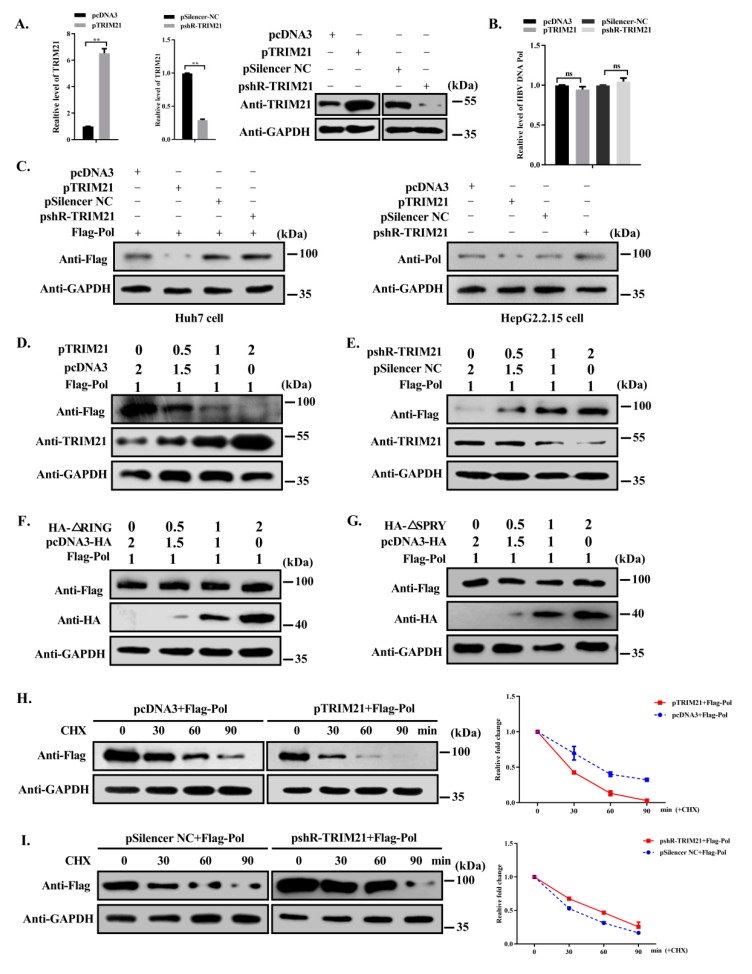
Figure 3.
TRIM21 negatively regulates the stability of HBV DNA Pol. (A) Huh7 cells were transfected with TRIM21 overexpression or knockdown plasmids or control, and the level of TRIM21 mRNA or protein in the cells was detected by RT-qPCR and Western blot. (B) FLAG-HBV DNA Pol was cotransfected with TRIM21 overexpression or knockdown plasmid. The mRNA level of HBV DNA Pol was detected by RT-qPCR. (C) Huh7 cells were transfected as described in (B), and HepG2.2.15 cells were transfected with TRIM21 overexpression or knockdown plasmids. Western blot was used to detect the protein level of HBV DNA Pol with anti-FLAG antibody or anti-Pol antibody. (D) Huh7 cells were transfected with FLAG-HBV DNA Pol along with increasing amounts of TRIM21 expressing plasmid, and WWestern blot was used to detect the protein level of HBV DNA Pol. (E) As described in (C), except for using pshR-TRIM21 plasmid. (F) As described in (C), except for using TRIM21-ΔRING plasmid. (G) As described in (C), except for using TRIM21-ΔSPRY plasmid. (H) Huh7 cells were cotransfected with FLAG-HBV DNA Pol and pcDNA3 or TRIM21 plasmid. Thirty hours later, 100μg/ml cycloheximide was used to treat cells, and the protein level of HBV DNA Pol was detected by Western blot. (I) Huh7 cells were cotransfected with FLAG-HBV DNA Pol and pSilencer NC or pshR-TRIM21. The treatment was the same as in (H). Data are representative of three independent experiments with three replicates each.