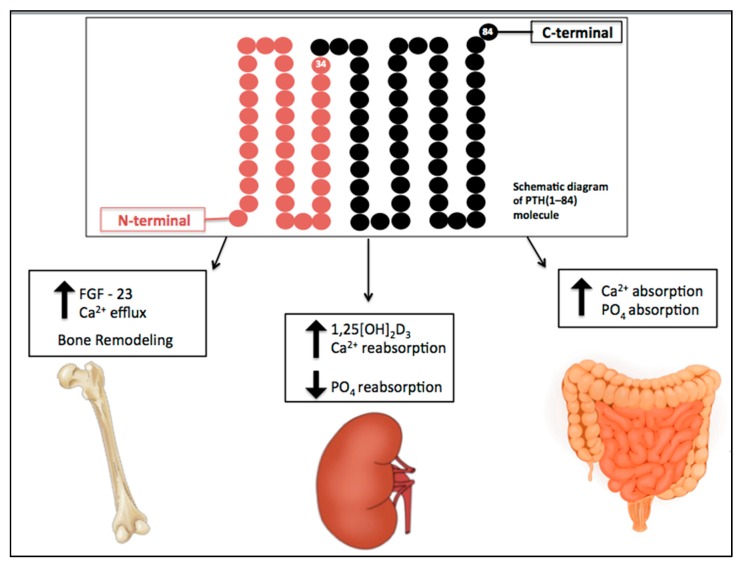
Figure 1.
Physiological actions of parathyroid hormone (PTH). PTH plays a key role in the maintenance of calcium levels. It stimulates bone turnover and calcium release from the skeleton. In renal tubular cells, PTH increases calcium reabsorption, inhibits phosphate reabsorption, and upregulates the 1α-hydroxylase gene, responsible for conversion of 25-hydroxyvitamin D to the active metabolite, 1,25[OH]2D3. It also enhances calcium and phosphate intestinal absorption by increasing the production of activated vitamin D. Down arrow = decrease, Up arrow = increase.