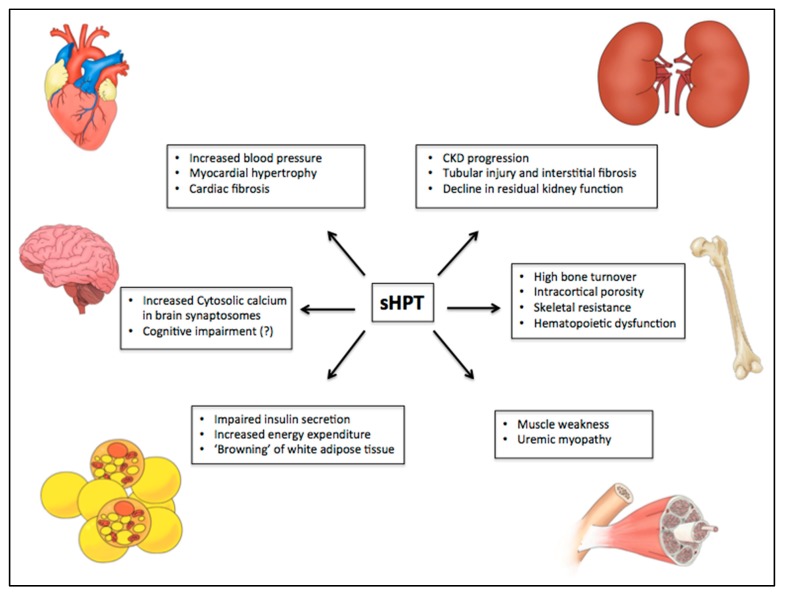
Figure 3.
PTH-related manifestations on different target organs in uremic syndrome. Some studies have suggested the role of PTH in uremic syndrome through calcium-dependent and independent mechanisms. Among several toxic actions, it has been shown an association of high levels of PTH with myocardial hypertrophy and cardiovascular disease, nervous system disorders, development of sarcopenia, progression of chronic kidney disease, hematopoietic dysfunction, reduced insulin secretion by pancreatic beta-cells, increase of energy expenditure, “browning” of white adipose tissue, and high bone turnover with significant cortical compartment loss. CKD: chronic kidney disease.