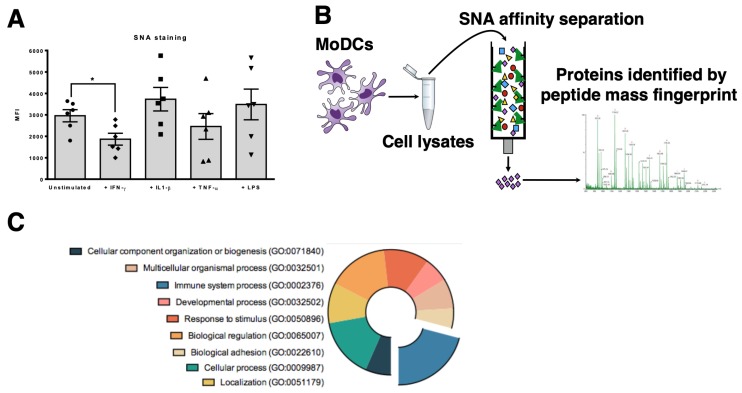
Figure 1.
Mass spectrometry analysis of SNA-binding proteins isolated from DCs reveals key immune-related proteins. (A) The reactivity of Sambucus nigra (SNA) lectin to α2,6-sialylated glycans on the surface of human DCs was quantified by flow cytometry after different maturation stimuli: IFN-γ, IL-1β, TNF-α and LPS. Unstimulated DCs were used as control. Values presented are mean ± SEM (N = 6). Statistically significant differences are indicated by asterisks (* p ≤ 0.05). (B) Schematic representation of the steps followed to identify α2,6-sialylated proteins from DCs. Whole cell lysates of human DCs were immunoprecipitated through a SNA-binding column. The eluted proteins were analyzed by mass spectrometry and the corresponding identified scores were matched and associated with Gene Ontology (GO) entries. (C) Distribution of the identified sialylated proteins by their molecular function. Pie chart represents different molecular functions of the identified proteins, according to the GO entries. Immune system processes were highlighted.