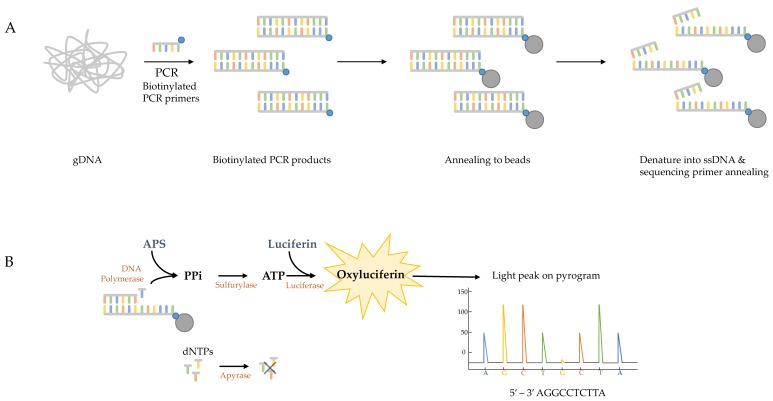
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of the pyrosequencing method. (A) Genomic DNA (gDNA) of clinical samples or fungal isolates are used as template in the initial PCR with biotinylated (blue dots) primers. The biotinylated PCR products are immobilized by annealing to streptavidin-sepharose beads (grey dots). The DNA strands are then separated allowing the sequencing primer to anneal to the ssDNA templates. (B) The four enzymes (polymerase, sylfurylase, luciferase and apyrase) and two substrates (adenosine 5’ phosphosulfate (APS) and luciferin) promote the production of light after nucleotide incorporation in every cycle, resulting in light peaks on the pyrogram that are representative of the DNA sequence. The excess nucleotides are degraded after each cycle by apyrase and the reaction solution is rejuvenated for the incorporation of the next nucleotide.