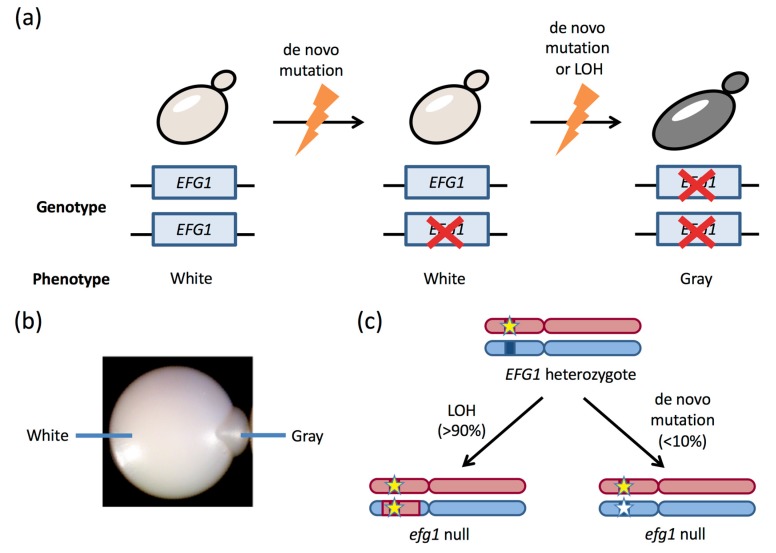
Figure 3.
Genetic events at the EFG1 locus can impact C. albicans phenotypes. (a) Most C. albicans isolates are diploid and carry two functional alleles of EFG1. However, one EFG1 allele can be disrupted by a de novo mutation, and the second allele can then be lost either by LOH or by a second de novo mutational event. Cells with functional EFG1 are in the ‘white’ state, whereas the complete loss of EFG1 function causes cells to adopt the ‘gray’ state. (b) Image of a single colony showing white efg1/EFG1 cells that have given rise to a sector of gray efg1 null cells. (c) Clinical isolates that are heterozygous for EFG1 can lose the functional EFG1 allele either by LOH (>90% of events) or de novo mutation (<10% of events). Asterisks indicate nonfunctional alleles.