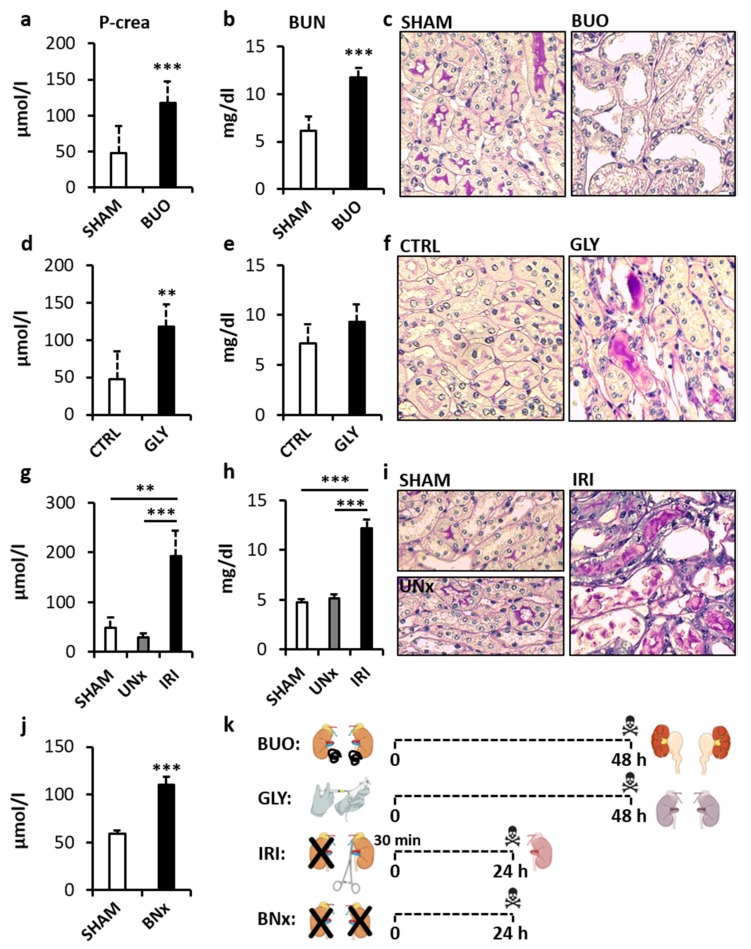
Figure 1.
Renal function and histopathological assessment of mice with acute kidney injury (AKI). Bilateral ureteral obstruction: (a) creatinine; (b) BUN; (c) left panel—normal renal architecture, right panel—tubular dilation and atrophy. Glycerol-induced AKI: (d) creatinine; (e) BUN; (f) left panel—normal renal architecture, right panel—tubular atrophy and proteinuric casts. Ischemia–reperfusion injury: (g) creatinine; (h) BUN; (i) left panel—normal renal architecture, right panel—tubular atrophy and dilation, epithelial cell necrosis and cell shedding, and proteinuric casts. Bilateral nephrectomy: (j) creatinine. Overview of the preparation of the individual models (k). BUO—bilateral ureteral ligation, BUN—blood urea nitrogen, GLY—glycerol-induced AKI, UNx—unilateral nephrectomy, IRI—ischemia–reperfusion injury, BNx—bilateral nephrectomy. ** denotes p < 0.01, *** denotes p < 0.001. Data are presented as mean + SD. Histological images show periodic acid Schiff stain (PAS), magnification 400x.