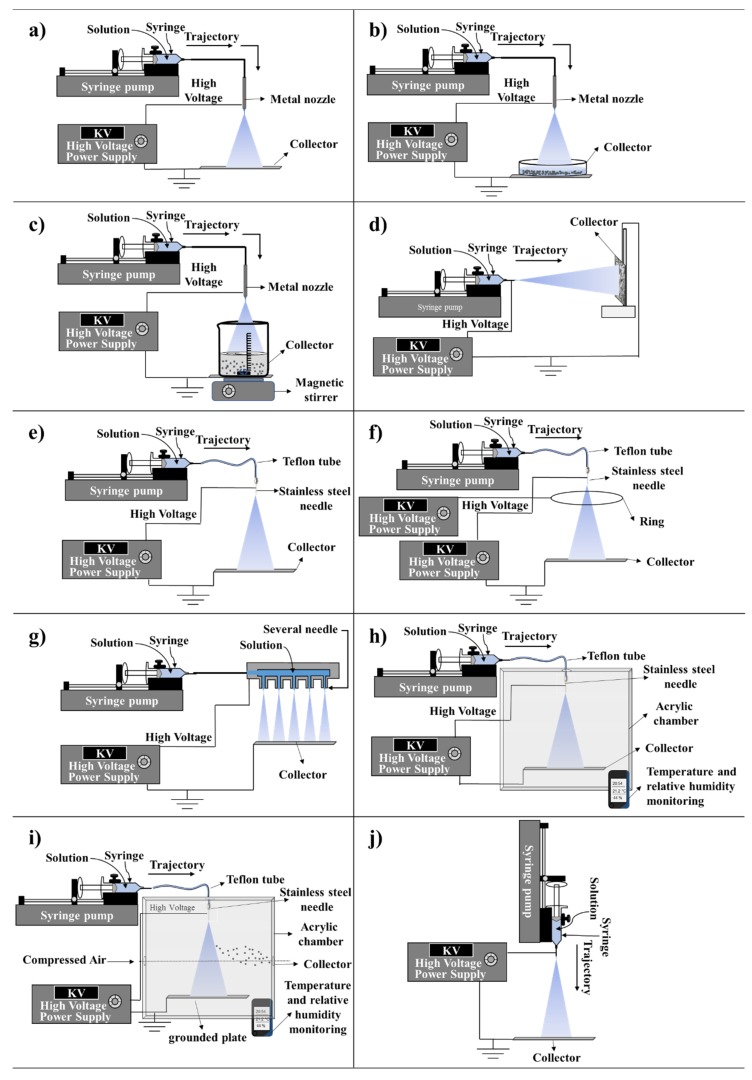
Figure 2.
The various configurations applied for the ES technique for the production of MPs. (a) The simplest ES setup consisting of a syringe pump connected to a capillary connected to a high voltage source and a collector to collect the MPs; (b) similar setup as (a) but with a different collector; (c) similar setup as (a) but with a different collector and a magnetic stirrer added; (d) similar setup as (a) but the syringe pump and collector are positioned horizontally; (e) similar setup as (a) but with an additional silicone tube transporter from the syringe to the needle; (f) similar setup as (e) but with an extra power supply and a ring connected to the high voltage; (g) a multiplexed ES (MultES) setting containing several nozzles; (h) an ES setting performed in a chamber providing control over the temperature and humidity; (i) ES setting similar to (h) but with additional horizontal airflow to promote the evaporation of an organic solvent; and (j) demonstrates an ES setting of vertical orientation in the absence of any tube transporter.