Table 50-2.
Indications, Doses, Adverse Effects, and Comments for Drugs Frequently Used in Cases of Acute Kidney Injury
| Drug | Indication | Dosage | Adverse Effects | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Furosemide | Fluid overload, oliguria/anuria, hyperkalemia | 2 to 5 mg/kg IV bolus, may be repeated three to five times; 0.5 to 1 mg/kg/hr CRI if urine production increased following bolus | Ototoxicity; volume depletion (unlikely if patient is monitored) | Results are frequently not satisfactory in cases of severe AKI but adverse effects minimal, so use in anuric AKI |
| Regular insulin | Hyperkalemia | 0.5 units/kg IV or IM, may be repeated every 4 to 6 hours, provided hypoglycemia is avoided | Hypoglycemia | Hypokalemic effect modest and transient; IV dextrose must be administered concurrent with and following insulin administration |
| Dextrose | Hyperkalemia; avoidance of hypoglycemia following insulin administration | IV bolus of 2 g/unit of insulin administered; bolus followed by CRI (the dextrose concentration and administration rate is dependent on serial blood glucose concentrations, patient's fluid status, and accessibility of central line) | Hyperglycemia, hyperosmolarity, hyponatremia, phlebitis with high dextrose concentrations | Dextrose should be diluted to avoid phlebitis; frequent changes in dextrose CRI frequently necessary based on serial blood glucose measurements |
| Calcium gluconate (10%) | Hyperkalemia; symptomatic hypocalcemia | 0.5 to 1.5 mL/kg of 10% solution or 50 to 150 mg/kg IV slowly, to effect, while monitoring ECG; may be repeated | Worsening bradycardia and ECG changes; hypercalcemia; soft tissue mineralization | ECG should be monitored during administration; will not affect extracellular potassium concentration; effective in rapidly normalizing ECG but results transient; administration of large volumes may contribute to soft tissue mineralization |
| Sodium bicarbonate | Severe acidemia |
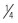 to to 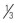 of the base deficit over 30 to 60 minutes, followed by an additional of the base deficit over 30 to 60 minutes, followed by an additional 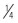 over the next 4 to 6 hours; additional dosing based on serial blood gas analyses over the next 4 to 6 hours; additional dosing based on serial blood gas analyses |
Paradoxical central nervous system acidosis, hypernatremia, fluid overload, hypochloremia; may cause or exacerbate hypokalemia if patient is polyuric; may exacerbate hypocalcemia | Requires close monitoring of blood gases and electrolytes for effective treatment and avoidance of adverse effects |
| Albuterol (inhaled) | Hyperkalemia | Four puffs; 90 microgram actuation via Aerokat device; repeated every 1 to 4 hours as necessary | Tachycardia, tremors, hyperexcitability | Adverse effects are uncommon at this dose; effects observed within 1 to 2 hours but may require multiple doses; effects can be sustained (several hours); only recommended for peracute hyperkalemia |
| Sodium polystyrene sulfonate | Hyperkalemia | 2 g/kg per day PO or via feeding tube, divided into three to four doses per day; dose can be adjusted to effect | Hypernatremia, constipation, colonic necrosis | Rarely used except in chronic dialysis patients |
AKI, Acute kidney injury; CRI, continuous rate infusion; ECG, electrocardiogram; IM, intramuscularly; IV, intravenously; PO, per os (orally).
