FIGURE 42-2.
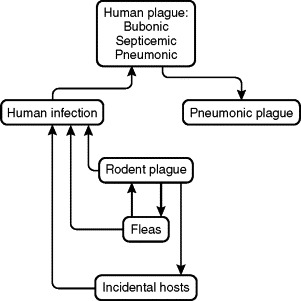
Yersinia pestis cycles, demonstrating the interrelationships of its rodent reservoir, flea vector, and incidental mammalian hosts, including humans. In the usual situation, Y. pestis is transmitted from rodent to rodent, and occasionally from rodent to human or other incidental mammalian host, by an infective rodent flea. Pet dogs and cats can bring infective rodent fleas into the home environment. Infection may be transmitted directly from rodent to rodent by cannibalism, and from infected animal to predator or to human by ingestion. Humans may also acquire infection by accidental percutaneous inoculation while handling contaminated tissues or fluids. Plague pneumonia can be transmitted from one person to another and, rarely, from cats to persons, by infective respiratory droplets.
