Figure 13-3.
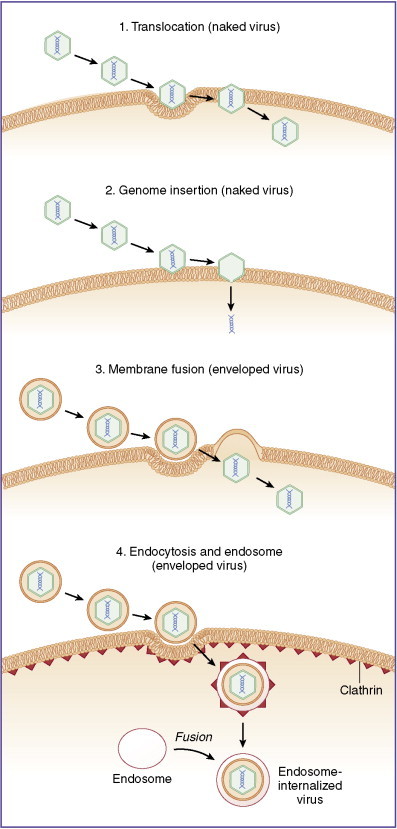
Viruses enter host cells following attachment by multiple means including (1) translocation, in which a virus crosses membranes intact; (2) genome insertion, in which attached viruses inject genetic material directly into cytoplasm; (3) membrane fusion, in which genomic contents of a virus are dumped into the host cell cytoplasm; and (4) endocytosis dictated by surface receptor binding and clathrin-mediated transport, sometimes leading to fusion into intracellular endosomes.
