Figure 6.
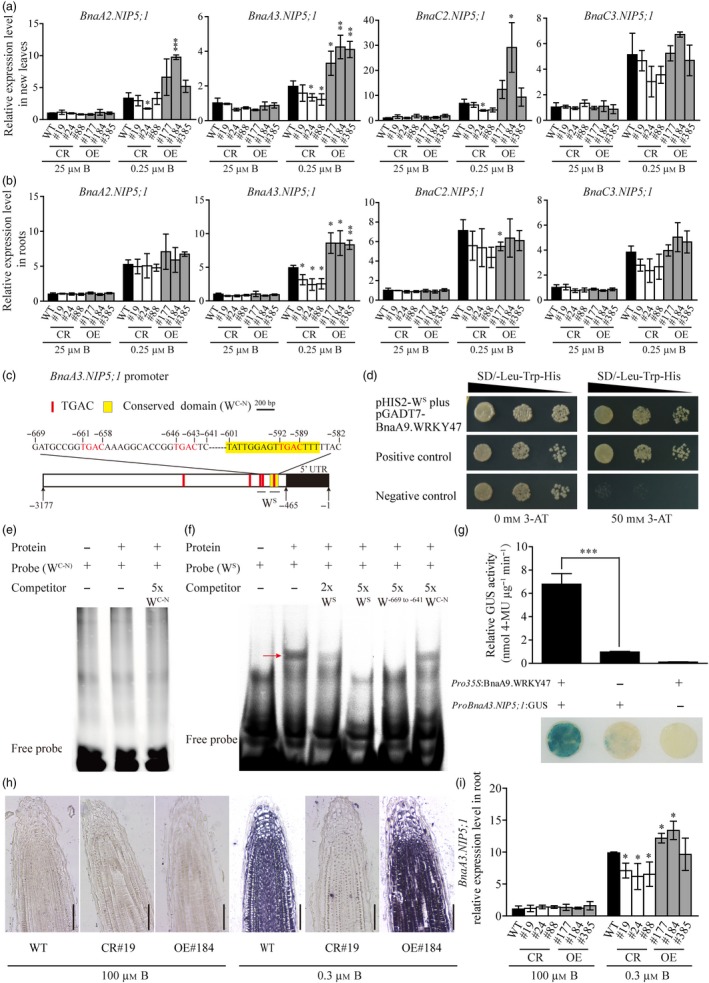
BnaA9.WRKY47 directly activates the expression of BnaA3.NIP5;1. (a‐b) qRT‐PCR analysis of BnaNIP5;1s expression in the new leaves and roots of the wild‐type ‘Westar 10’, BnaA9.WRKY47 mutants and overexpressing plants. Gene expression was normalized by BnaEF1α and BnaTubulin mRNAs with three biological replicates. Asterisks indicate significant differences in gene expression levels between BnaA9.WRKY47 transgenic lines and ‘Westar 10’ (t‐test, * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001). (c) Characterization of the BnaA3.NIP5;1 promoter sequence. The TGAC core sequence and conserved sequence WC‐N of BnaNIP5;1s were marked by a red and yellow rectangle, respectively. The specific sequence WS of BnaA3.NIP5;1 was shown. (d) The interaction of BnaA9.WRKY47 protein with BnaA3.NIP5;1‐specific promoter region (WS) in yeast. (e‐f) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay to analyse the interaction of BnaA9.WRKY47 and the conserved WC‐N in BnaNIP5;1s (e) or the specific WS (f) in the BnaA3.NIP5;1 promoter. The 5′ Cy5 labelled probe was incubated with BnaA9.WRKY47‐His protein at 25°C for 20 min. Competition for the labelled sequences was tested by adding different concentrations of unlabelled probes. The binding shift is indicated with a red arrow. (g) Transient expression assay of BnaA3.NIP5;1 activated by BnaA9.WRKY47 in tobacco leaves. GUS activities were detected after 35S:BnaA9.WRKY47 and proBnaA3.NIP5;1:GUS were injected into tobacco leaves together or separately for 2 days. Values represent mean values ± SD of three biological replicates, and two independent experiments verified these results. Asterisks indicate significant differences based on a t‐test (*** P < 0.001). (h) In situ hybridization analysis of BnaA3.NIP5;1 expression in the root tips of BnaA9.WRKY47 transgenic plants. Longitudinal sections of the root tips from wild‐type, CR#19 and OE#184 seedlings grown on solid medium containing 100 µm B or 0.3 µm B for 5 days. The root tips were hybridized with BnaA3.NIP5;1‐specific antisense probe labelled with DIG. Bars = 100 µm. (i) qRT‐PCR analysis of BnaA3.NIP5;1 expression in the roots of the BnaA9.WRKY47 transgenic plants grown on solid medium containing 100 µm B or 0.3 µm B for 5 days. Gene expression was normalized by BnaEF1α and BnaTubulin mRNAs with three biological replicates. Asterisks indicate significant differences in gene expression levels between BnaA9.WRKY47 transgenic lines and ‘Westar 10’ (t‐test, * P < 0.05).
