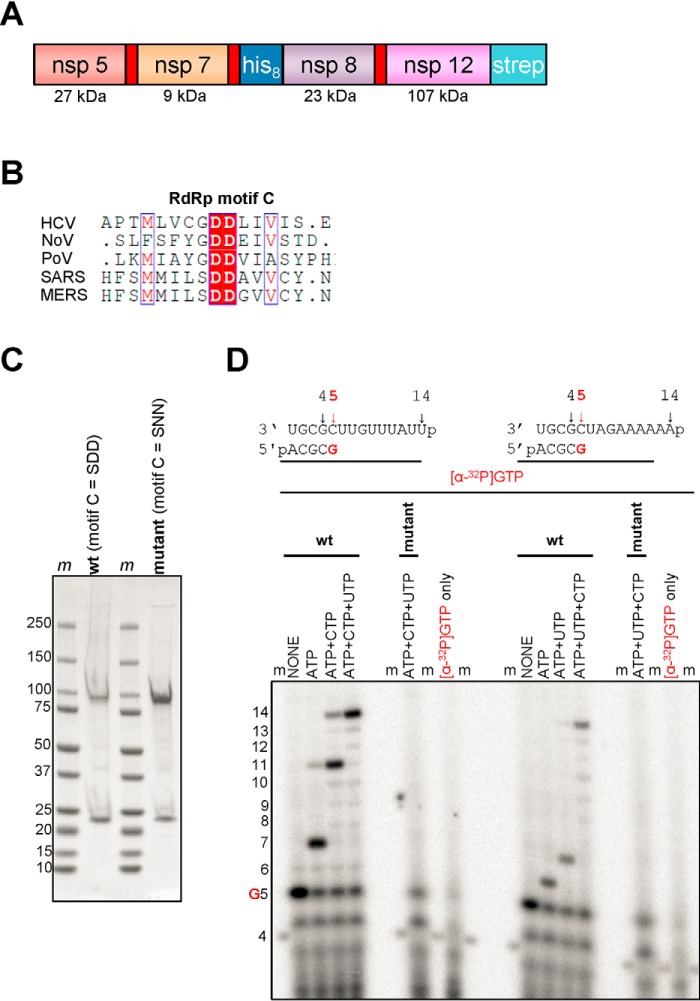
Figure 1.
Expression, purification, and characterization of the MERS RdRp complex. A, the construct contains nonstructural proteins nsp5, nsp7, nsp8, and nsp12. Red rectangles indicate original nsp5 protease cleavage sites. His8 and Strep indicate the locations of histidine and strep tags, respectively. B, a snapshot of a sequence alignment (T-Coffee) of representative RdRp enzymes from positive-sense RNA genome viruses illustrating sequence conservation within RdRp motif C. C, SDS-PAGE migration pattern of the purified enzyme preparations stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 dye. Proteins migrating at ∼100 and ∼25 kDa contain nsp12 and nsp8, respectively. D, RNA synthesis on a short model primer/template substrate. Template and primer were both phosphorylated (p) at their 5′-ends. G indicates incorporation of the radiolabeled nucleotide opposite template position 5. RNA synthesis was monitored with the purified MERS RdRp complex wt (motif C = SDD) and active-site mutant (motif C = SNN) in the presence of NTP combinations designed to generate specific products. Lanes m illustrate the migration pattern of the radiolabeled 4-nucleotide-long primer. HCV, hepatitis C virus; NoV, norovirus; PoV, poliovirus.