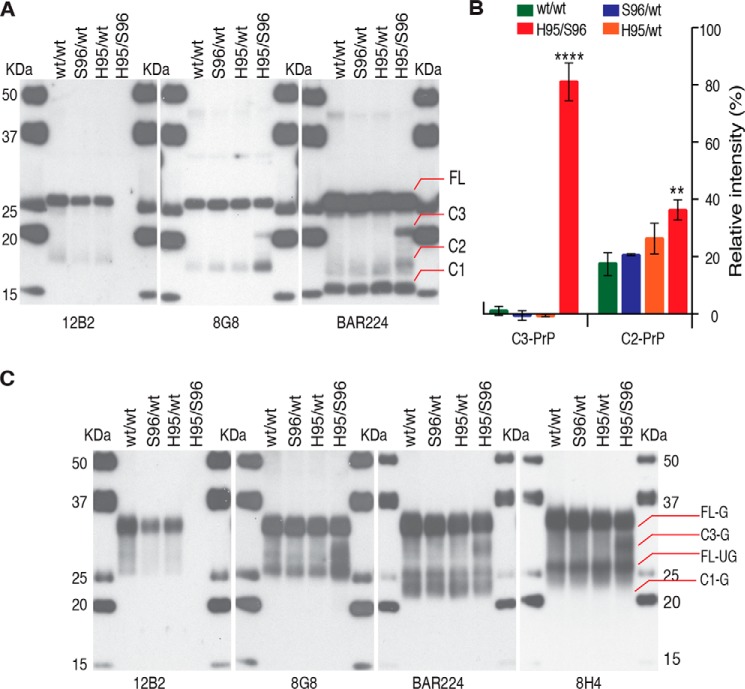
Figure 2.
Alternative N-terminal endoproteolytic processing and antibody reactivity of total PrP in brain of CWD-infected deer expressing different PrPC allelotypes. A, de-glycosylated total PrP in Wisc-1–infected white-tailed deer expressing WT-(Q95G96)–PrPC, Ser-96–PrPC, or His-95–PrPC allelotypes. His-95/Ser-96 deer accumulated a distinctive N-terminally–cleaved PrP (C3) of ∼20 kDa following removal of glycans with PNGase F. Full-length (FL) PrP, C-terminal PrP (C1, C2, and C3). B, percentage of de-glycosylated C3- and C2–PrP detected with BAR224. Mean with standard deviation is indicated by bars. Densitometry was performed in three separate de-glycosylation experiments for each individual deer CWD lineage. The brain of His-95/Ser-96 deer contained significantly higher levels of C3- and C2–PrP than other deer. ANOVA, p < 0.05. Differences in C2–PrP abundance were 4–5-fold larger with 8G8 (data not shown). C, total deer brain PrP (G, glycosylated; UG, unglycosylated). The mAb 12B2 (epitope WGQGG, deer residues 93–97) does not recognize Ser-96–PrPC or His-95–PrPC. The abundance of full-length and C1-PrP between deer was equivalent ruling out post-homogenization degradation.