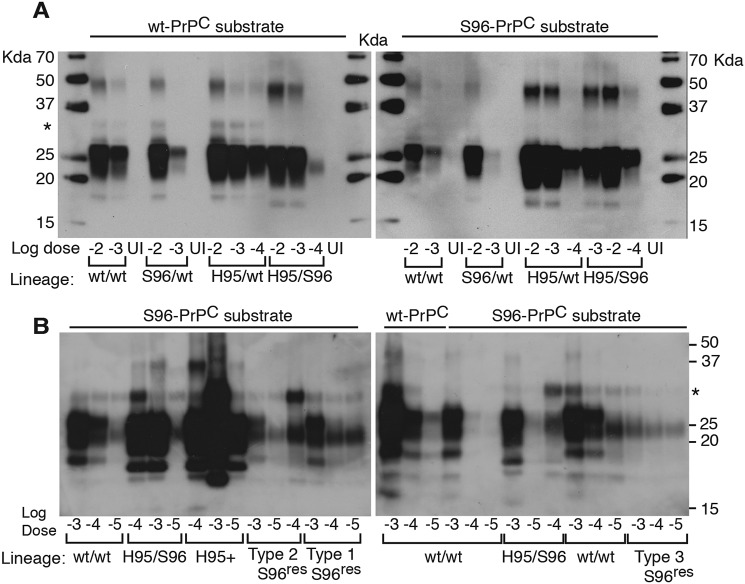
Figure 9.
In vitro amplification of CWD lineages from deer and tg60 mice. A, PMCA propagation of CWD lineages on WT–PrP and Ser-96–PrPC substrates from tg33 and tg60 brains. Reactions in WT–PrPC substrate seeded with WT/WT, Ser-96/WT, and His-95/WT prions amplified PrP-res pattern consistent with the Wisc-1 strain. In vitro conversion of Ser-96–PrPC produced the Wisc-1 pattern when seeded with WT/WT and Ser-96/WT prions and the H95+ pattern when seeding was done with His-95/WT and His-95/Ser-96 CWD lineages. Accumulation of a high-molecular mass (30 kDa) PK-res PrP was also observed (asterisk). Amplification was a single 24-h round of PMCA. Uninfected control (UI) was seeded at 10−2. B, unstable replication of S96res PrPCWD types 1 and 2 during a single 48-h round of PMCA (left panel). Type 3 S96res was amplified unaltered (right panel). PMCA of Wisc-1 (WT/WT) prions on Ser-96–PrP also produced type-3 PrPCWD when seeded at larger dilutions. His-95/Ser-96 and tg60P1His-95/Ser-96 prions (i.e. H95+) were more stable generating the low molecular weight PK-res PrPCWD characteristic of this strain. Each panel shows PMCA reactions seeded at the same time and amplified in separate sonicators. Amplification conditions: 30 s sonication at 60% amplitude every 15 min at 37 °C. Western blotting detection of PrP-res was achieved with BAR224 (1:10,000) and Sha31 (1:30,000) mAbs (A and B, respectively).