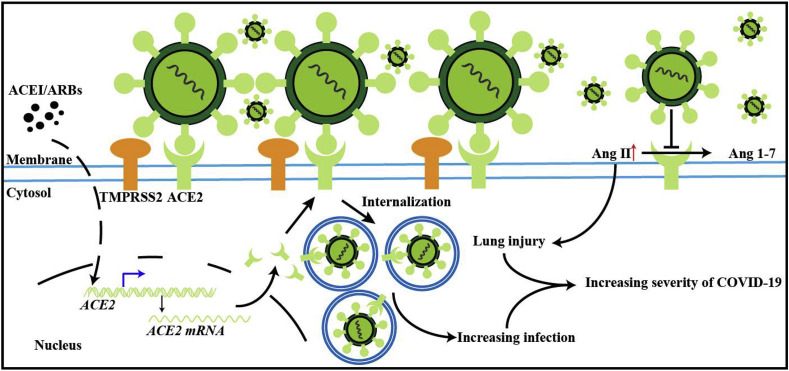
Fig. 5.
Effect of ACE2 and ARBs on SARS-CoV-1 or SARS-CoV-2 infection. This illustrates a proposed mechanism of the effects of ACE2 in COVID-19 infection. SARS-COV-2 virus uses the ACE2 receptor to gain entry into the cell, leading to the increase in proinflammatory cytokines and the development of cytokine storm, as well as increased viral replication (see Fig. 4). TMPRSS2 assists in S protein priming. ARBs may potentially increase the expression of ACE2, leading increased binding of SARS-CoV-2 and greater proinflammatory cytokine production. SARS-CoV-2 may at the same time downregulate ACE2, which leads to an increase in angiotensin 2 mediated lung injury. The negative regulatory activity of ACE2 is reduced by SARS-CoV-2 and leads to worsening severity of illness.