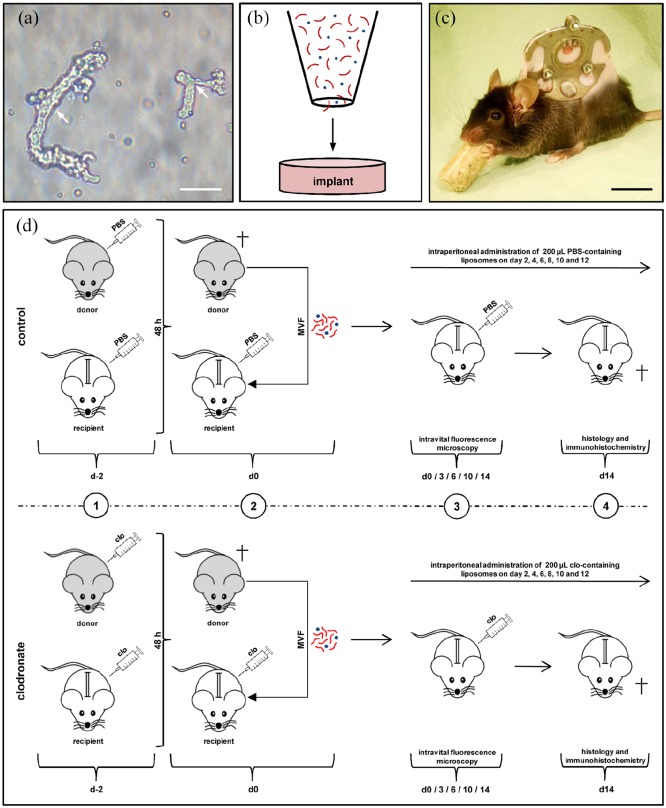
Figure 1.
Model and experimental study design. (a) Freshly isolated MVFs (arrows) from the epididymal fat pads of a GFP+ donor mouse. Scale bar: 40 µm. (b) Schematic illustration of collagen–glycosaminoglycan matrix seeding with MVFs (red) and single cells (blue). (c) C57BL/6 mouse with a dorsal skinfold chamber containing a full-thickness skin defect. Scale bar: 17.5 mm. (d) Schematic overview of the experimental protocol of the present study. 1: GFP+ donor mice and GFP− recipient mice were treated with liposomes containing clo or PBS 48 h prior to MVF isolation (day −2). 2: MVFs were harvested from the epididymal fat pads of the donor animals, seeded onto collagen–glycosaminoglycan matrices and implanted into full-thickness skin defects within dorsal skinfold chambers of GFP− recipient mice, which were again treated with clo- and PBS-containing liposomes. 3: The recipient animals further received intraperitoneal injections of clo or PBS on days 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and 12. The implants were microscopically analyzed on day 0, 3, 6, 10, and 14. 4: At the end of the 2-week observation period, the dorsal skinfold chamber preparations were processed for further histological and immunohistochemical analyses.