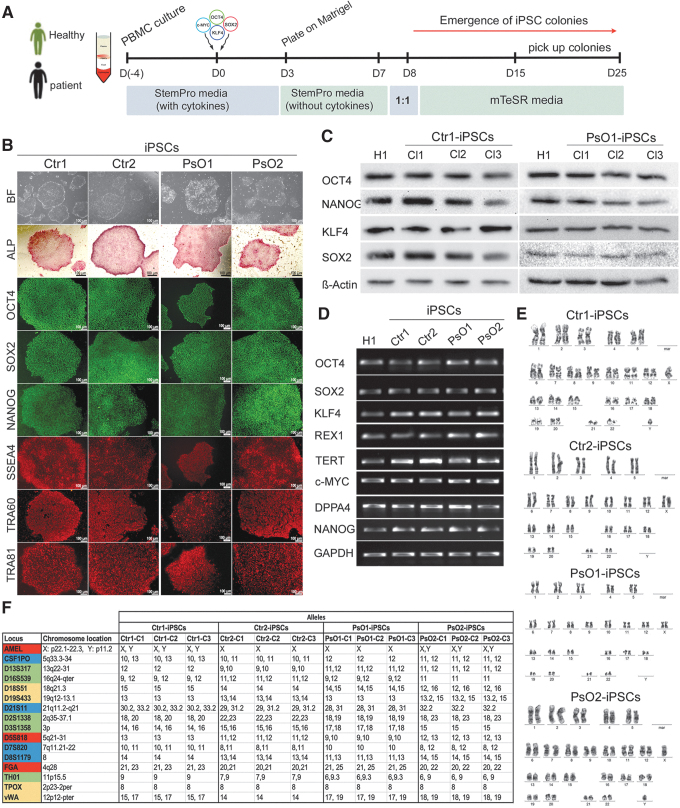
FIG. 1.
Generation and characterization of iPSC lines. (A) Schematic diagram of the protocol used for iPSCs generation. PBMCs were reprogrammed using cytotune 2.0 Sendai reprogramming kit. (B) Representative images showing the characterization of iPSCs generated from healthy controls (Ctr-iPSCs) and patients (PsO-iPSCs). The generated iPSCs showed hESC-like morphology, strong alkaline phosphatase activity (ALP), and expressed the pluripotency markers (OCT4, SOX2, NANOG, SSEA4, TRA-60, and TRA-81). (C) Western blotting showing the expression of pluripotency markers OCT4, NANOG, KLF4, and SOX2. (D) RT-PCR analysis of the generated iPSCs showing the expression of the pluripotency markers, OCT4, SOX2, NANOG, KLF4, REX1, TERT, DPPA4, and c-MYC. H1-hESCs were used as control. (E) Representative iPSC lines (Ctr1-iPSCs, Ctr2-iPSCs, PsO1-iPSCs, and PsO2-iPSCs) showed normal karyotype by G-banding analysis. (F) Genetic profiling of the generated iPSCs from healthy and psoriatic patients through the STR analysis showed that the iPSCs from each individual are typically identical. Scale bars = 100 μm. hESCs, human embryonic stem cells; iPSC, induced pluripotent stem cell; PBMCs, peripheral blood mononuclear cells; RT-PCR, reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; STR, short tandem repeat.