Figure 2.
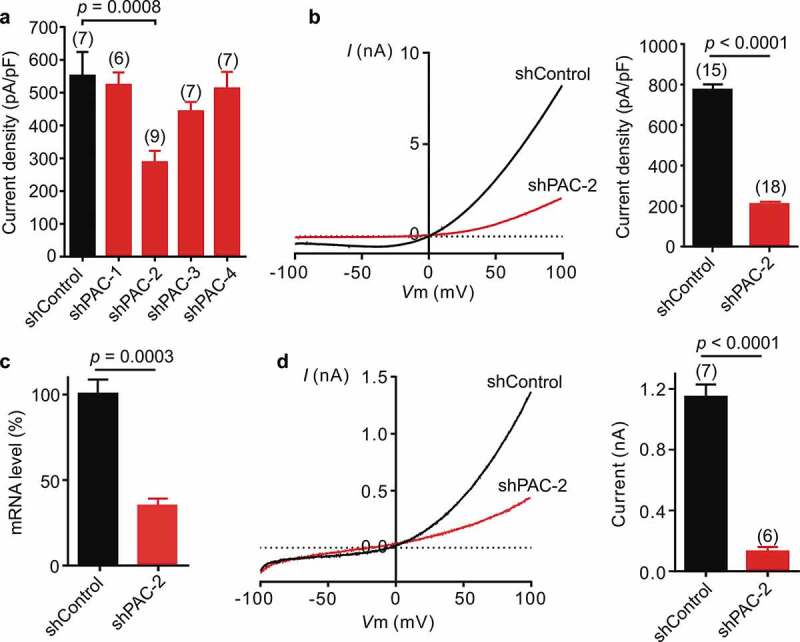
Knockdown of Pac markedly reduced the proton-activated Cl− currents in rat cells. (a), Screening for shRNA targeting rat Pac in rat INS-1E cells by measuring extracellular pH 4.6-induced current densities (mean ± SEM) at +100 mV 3 days after shRNA transfection (one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Bonferroni post hoc test). (b), Example (left) and quantification (right) of pH 4.6-induced currents for rat INS-1E cells 4 days after shRNA transfection. Bars represent mean ± SEM (two-tailed Student’s t test). (c), shPAC-2-mediated Pac mRNA knockdown (mean ± SEM, n = 4 biological replicates) in primary rat cortical neurons assayed by qPCR. Expression levels were normalized to cells transduced with control shRNA as 100%. (d), Representative whole-cell currents at pH 4.6 monitored by voltage ramp protocol for shPAC-2-treated primary neurons. Background-subtracted current densities (mean ± SEM, two-tailed Student’s t test) at pH 4.6 and +100 mV for shPAC-2-treated primary rat neurons.
