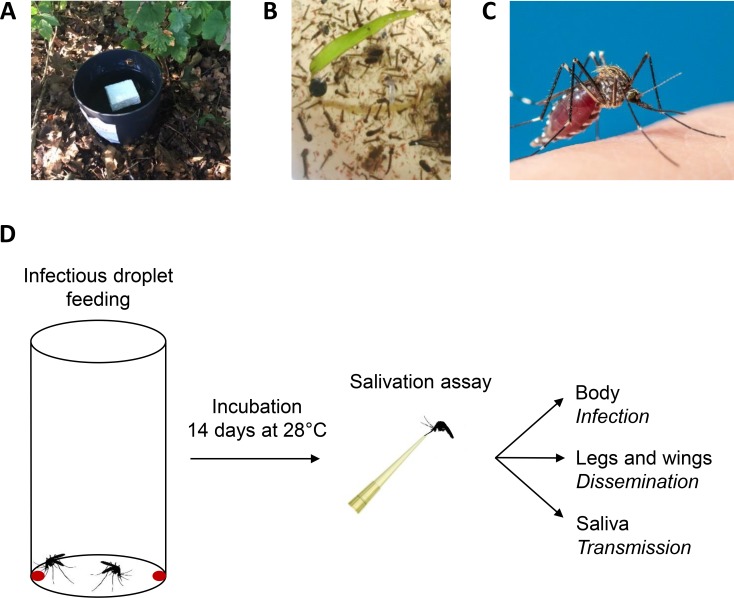
Fig 1. Ae. japonicus mosquito collection and the infectious droplet feeding experiment.
(A) Mosquito eggs were collected using oviposition traps. (B) Mosquito larvae were collected from local rain barrels. (C) An adult female mosquito, which was captured during human landing catches. (D) Infectious droplet feeding and subsequent salivation assays were performed to determine the vector competence of Ae. japonicus females for ZIKV and USUV.