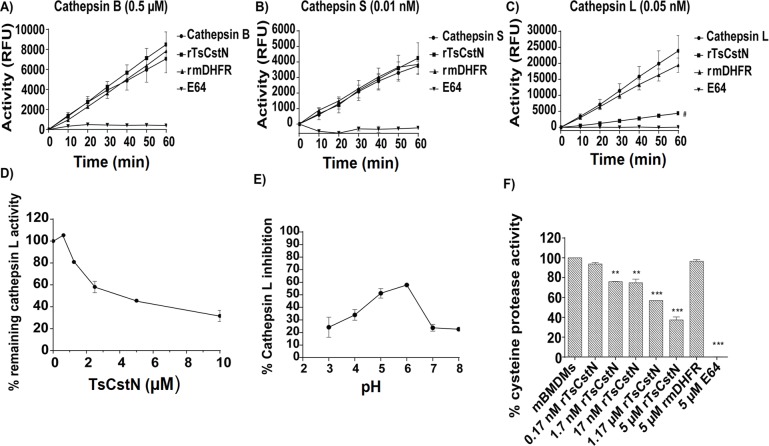
Fig 5.
Inhibitory activity of rTsCstN against Cat B (A), Cat S (B), and Cat L (C) demonstrated that rTsCstN specifically inhibited CatL activity but not that of CatB and CatS. rTsCstN could inhibit CatL activity in a dose-dependent manner (D). rTsCstN could inhibit CatL activity at the maximum at pH 6, followed by pH 5 (E). rTsCstN partially inhibited cysteine protease activity in mBMDM lysate to hydrolyze a fluorogenic substrate of CatL and CatS, Z-Phe-Arg-AMC, in a dose-dependent manner (F). E64 inhibitor, used as a positive control, completely inhibited CatB, CatS, and CatL activities. Irrelevant control (rmDHFR) could not inhibit any of CatB, CatS, and CatL activities. The result reported as mean ± SD. The experiments were performed in triplicate with three independent experiments. One-way ANOVA followed by a Bonferroni multiple comparison test were used for analysis: #p < 0.05, represents difference between CatL activity inhibited by rTsCstN and CatL activity only; **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001, represent differences between mBMDM lysate treated with dose-dependent manner of rTsCstN and cysteine protease activity in mBMDM lysate only.