Figure 1. Diagrams of the cassettes used in a TRACE system.
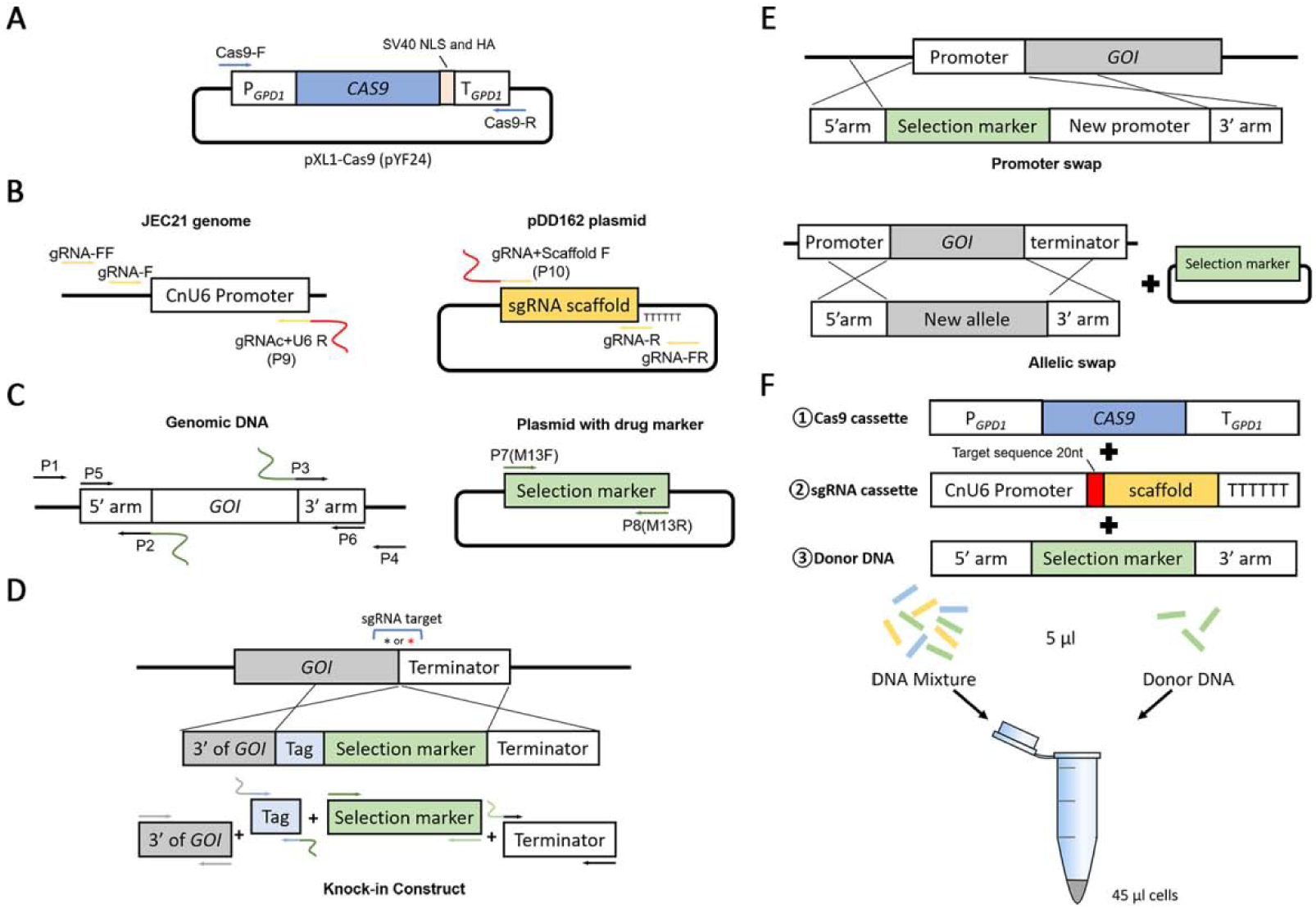
A. The simplified layout of the pXL1-Cas9 (pYF24) plasmid. The Cas9 construct (~7kb) for TRACE is amplified from this vector with the Cas9-F/Cas9-R primer set. B. The gRNA construct is amplified by fusing the U6 promoter and the gRNA scaffold in an overlap extension PCR with primers gRNA-F/gRNA-R. The U6 promoter and the gRNA scaffold are amplified from the genomic DNA of strain JEC21 and the vector pDD162 respectively. C. The gene deletion construct is amplified with the primer set P5/P6 by fusing the 5’ arm, the selection marker, and the 3’ arm in a double-joint PCR. The homologous arms are amplified from the genomic DNA of the parent strain and the drug selection marker is amplified from a vector with the M13F/M13R primer set. D. The native-tagging knock-in construct is generated by fusing 4 fragments: the 3’ end of GOI, the tag cassette, the selection marker, and the downstream of GOI (terminator). Asterisks indicate the locations of the gRNA target sequences. E. Both promoter swap and ORF allelic swap constructs contain two homologous arms in the donor construct. However, in allelic swap, the selection marker needs to be co-transformed into cell separately. F. The linear Cas9, gRNA, and donor DNA are co-transformed into Cryptococcus cells in the TRACE system.
