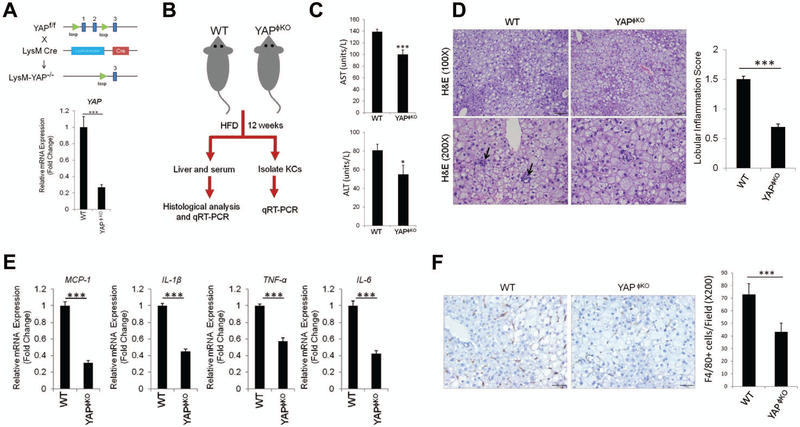
Figure 2. Deletion of YAP in Kupffer cells/macrophages reduces hepatic inflammation.
(A) Mice with macrophage/monocyte-specific deletion of YAP (YAPϕKO mice) were generated by crossing YAPfl/fl mice with LysM Cre mice. The expression of YAP in Kupffer cells isolated from YAPϕKO and their matched littermate control mice (LysM Cre−; YAPfl/fl or YAPfl/+) were determined by qRT-PCR analysis (Bottom panel). (B) Schematic outline of experimental approaches and analyses. (C) The levels of serum transaminases (AST and ALT) measured from YAPϕKO (n=5) and WT mice (n=11) fed HFD (mean±S.E.M.). (D) H&E staining and lobular inflammatory score of liver tissues (mean±S.E.M.). (E) qRT-PCR analysis for inflammatory cytokines in the liver tissues from HFD-fed WT (n=4) and YAPϕKO mice (n=6). (F) Immunohistochemical staining for F4/80 in liver tissues. The numbers of F4/80-positive Kupffer cells per 200X field were counted (mean±S.E.M.). The qRT-PCR data are expressed as mean±S.D. ***P<0.001.