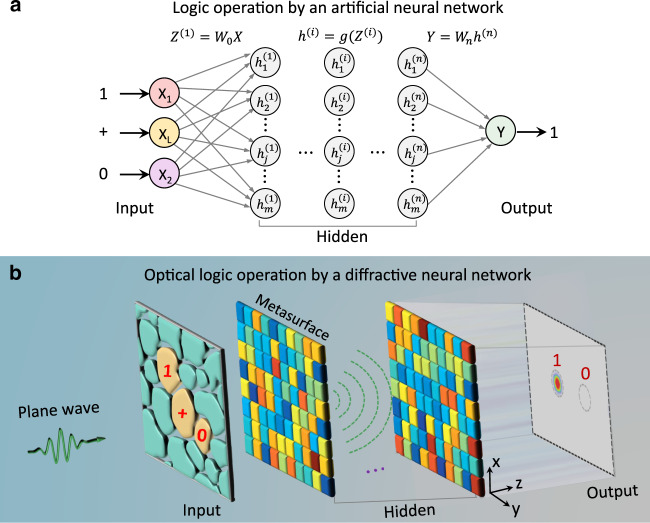
Fig. 1. Schematic illustration of optical logic operations by a diffractive neural network.
a Layout of a conventional artificial neural network for electron-based logic operations. b Layout of a diffractive neural network for photon-based logic operations. In b, each region at the input layer is assigned with a specific logic operator or an input logic state, and it has two different states for the transmittance of light. That is, the input layer can spatially encode the input plane wave for a specific optical logic operation, simply by setting the transmittance state of each region. The hidden layers, composed of metasurfaces, are designed to decode the encoded input light and generate an output optical logic state. In other words, the metasurface directionally scatters the encoded light into one of the two small designated regions at the output layer