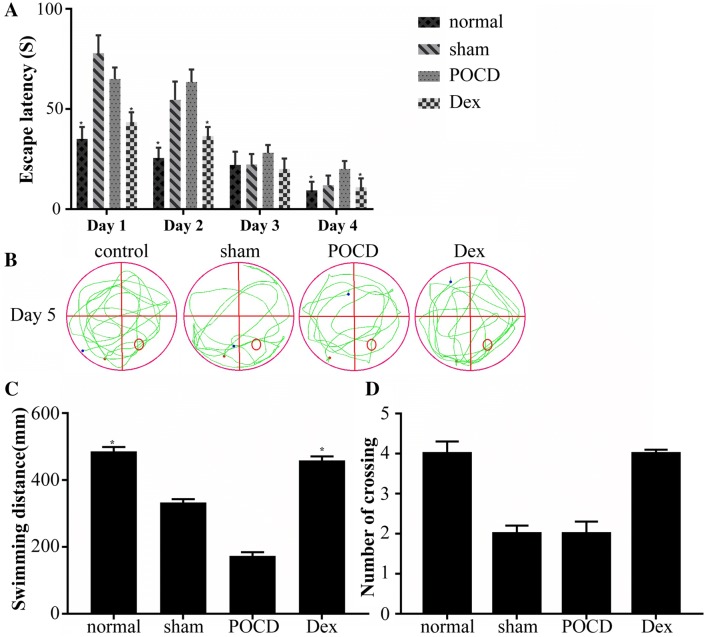
Fig. 1.
Results of Morris Water Maze test among rats from control group (N = 3), sham group (N = 3), postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD) group (N = 3) and dexmedetomidine (Dex) group (N = 3). a Escape latency time (the time from launch to the first landing on the platform) of rats in each group. The escape latencies of rats in the Dex group were significantly lower than those of the POCD group on day 2 and day 4. b The maps of computer printouts of the swimming trajectories in the probe test day of each group. c The total swimming distance by rats in the water for 90 s. The swimming distance of the rats treated with Dex was increased compared with those of POCD group. d Number of crossings over the original platform position by rats. Dex treatment significantly increased the crossing number compared with POCD group. One-way ANOVA was used to analyze the data and this analysis was followed by Tukey’s analysis. *Indicates a significant difference of p < 0.05 relative to the sham group