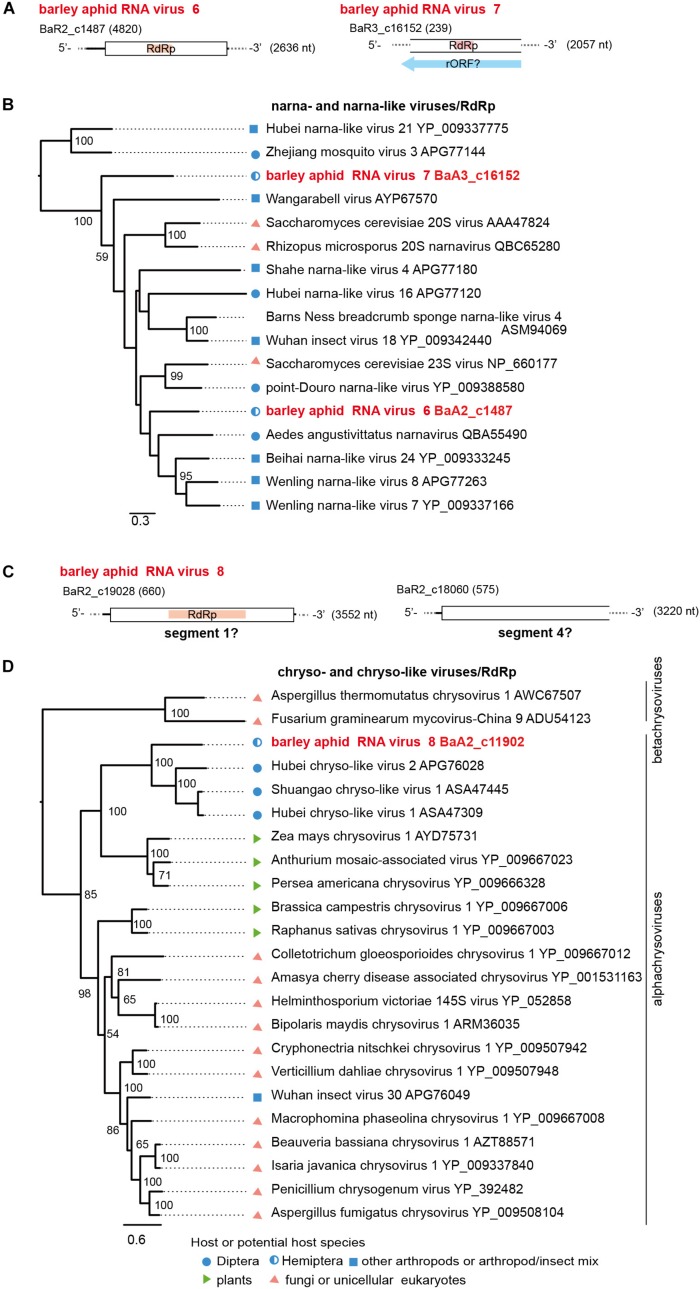
FIGURE 6.
Genome organizations and phylogenetic relationships of narna- and narna-like viruses (A,B) and chryso-and chryso-like viruses (C,D). (A,C) The genome structures of two novel narna-like viruses (named barley aphid RNA virus 6 and 7, BARV-6 and -7) in panel (A) and a chryso-like virus (named barley aphid RNA virus 8, BARV-8) in panel (C). rORF: reverse-frame ORF. (B,D) Phylogenetic relationships of two novel narna-like viruses BARV-6 and -7, yeast narnaviruses and invertebrate narna-like viruses (B), and BARV-8, chrysoviruses (the members of genus Alphachrysovirus) and chryso-like viruses (D). The ML trees were constructed using multiple amino acid sequence alignments of the RdRp sequences. Two narna-like viruses (Zhejiang mosquito virus 3 and Hubei narna-like virus 21) (B) or some members of genus Betachrysovirus (D) were used as the outgroups, respectively. The scale bar represents amino acid distances. The numbers at the nodes are bootstrap values of >50%.