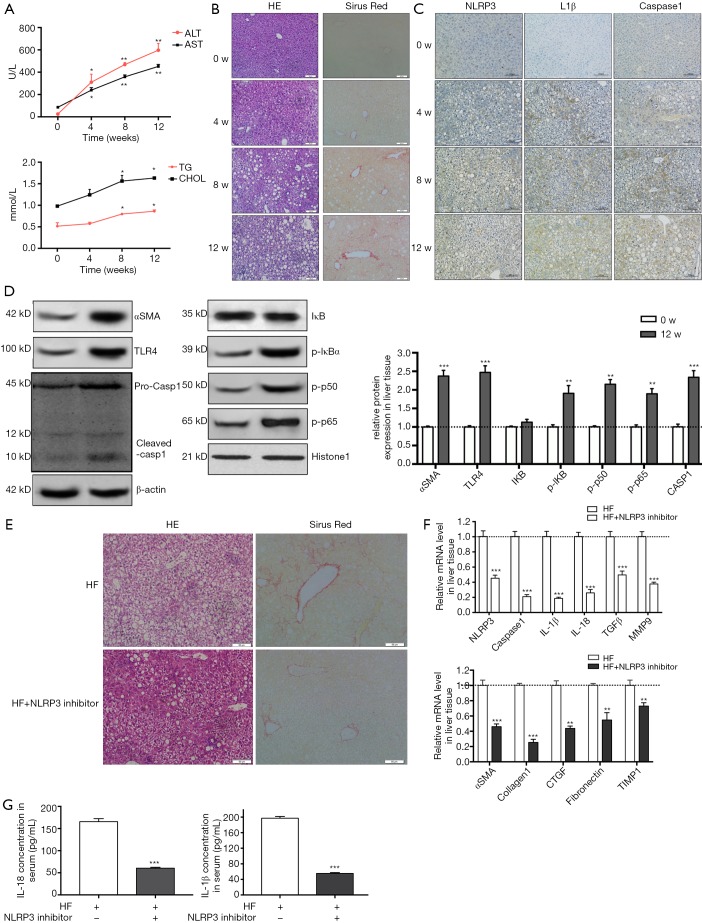
Figure 5.
NLRP3 inflammasome activation by TLR4-NFkB signalling pathway augments the development of NASH to fibrosis in HF-fed rats. Four weeks old SD rats were fed either an HF diet or normal chow for 12 weeks. Rats were euthanized, liver and blood were harvested at different time points (0, 4, 8 and 12 w). (A) The serum transaminase and triglycerides and cholesterol levels were evaluated. (B) HE and Sirus red staining in liver sections showed increased fat and collagen deposition at 4, 8 and 12 w. (C) Immunohistochemistry of NLRP3, IL-1β and caspase 1 at different time points. (D) aSMA, TLR4, NF-κB and caspase 1 protein expression in liver tissue from normal diet group and HF diet group. (E) In another experiment group, rats were fed with HF diet and meanwhile received either an intraperitoneal injection of NLRP3 inhibitor or saline, 5 mg/kg body weight for once every 3 days. After 12 w, rats were euthanized, liver and blood were harvested. (E) HE and sirus red staining in liver sections showed reduced fat and collagen deposition at the administration of NLRP3 inhibitor group. (F) mRNA levels of NLRP3, caspase 1, IL-1β, IL-18, TGFb, MMP9 and fibrotic makers were determined by RT-PCR. (G) IL-1β and IL-18 level in serum were measured. Results are presented as mean ± standard error. *, P<0.05, **, P<0.01 and ***, P<0.001 compared with control (untreated). Scale bar: (B) 50 µm, (C) 100 µm, (E) 50 µm.