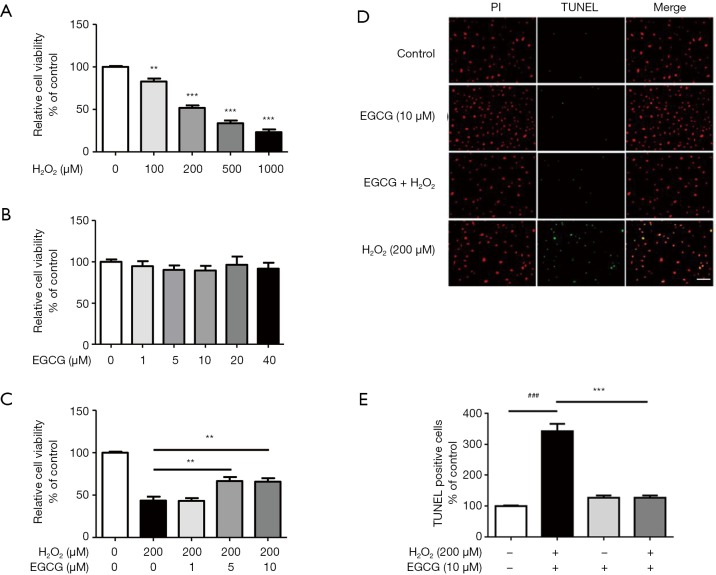
Figure 1.
The protective effect of EGCG on H2O2-induced decreased cell viability in HUVECs. (A) HUVECs were incubated with increasing concentrations of H2O2 (100–1,000 µmol/L). n=3. **, P<0.01, ***, P<0.001 vs. control group. (B) Effect of different concentration of EGCG on the viability of HUVECs. (C) Effect of EGCG pretreatment on the viability of HUVECs treated with H2O2. HUVECs were exposed to various concentrations of EGCG (1, 5, 10 µmol/L) for 24 h. Then, cells were treated with H2O2 (200 µmol/L) for 4 h and cell viability was tested by MTS assay. n=3. **, P<0.01 vs. H2O2 alone treatment group. (D) Representative staining with TUNEL and PI. (E) The number of TUNEL-positive nuclei was expressed as a percentage of the total nuclei detected. n=5. ###, P<0.001 vs. control group, ***, P<0.001 vs. H2O2 alone group. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM.